- Aide de Scilab
- Chaînes de caractères
- ascii
- asciimat
- blanks
- char
- convstr
- emptystr
- evstr
- grep
- isalphanum
- isascii
- isdigit
- isletter
- isnum
- justify
- length
- part
- prettyprint
- regexp
- sci2exp
- strcat
- strchr
- strcmp
- strcspn
- strindex
- string
- stripblanks
- strncpy
- strrchr
- strrev
- strsplit
- strspn
- strstr
- strsubst
- strtod
- strtok
- tokenpos
- tokens
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
prettyprint
Converts a Scilab object into some corresponding LaTeX, TeX, MathML or HTML strings
Syntax
str = prettyprint(a) str = prettyprint(a, exportFormat) str = prettyprint(a, exportFormat, delimiter) str = prettyprint(a, exportFormat, delimiter, processByElement) str = prettyprint(a, exportFormat, delimiter, processByElement, isWrapped)
Arguments
- a
a Scilab object.
- Supported types: booleans, encoded integers, real or complex numbers, polynomials and rationals with real or complex coefficients, strings, cells, linear dynamical systems (as generated with syslin()), other Tlists.
- Supported sizes: scalar, vector, matrix. Hypermatrices are not supported (only the first page is processed.)
- exportFormat
is the output format. Possible case-insensitive values are 'latex' (default), 'tex', 'mathml', 'html', or 'html4'.
- delimiter
is a string indicating the delimiter type to bracket the whole resulting matrix. It is only used if
processByElementis false. It can be '(' (default), '{', '[', '|', '||', or '' if no bracketing is required.In HTML, the '_' delimiter value can be used to format the input matrix without delimiter but with cells borders.
 Delimiters used for the components defining a linear dynamical system are always "(" and ")", even with
Delimiters used for the components defining a linear dynamical system are always "(" and ")", even withdelimiter="", unlessexportFormat="html4" is used: Then, "|" is imposed as inner syslin delimiter. This is useful when the result must be rendered in a Scilab GUI likemessagebox(), that supports only a restricted version of HTML.4- processByElement
is a boolean: If set to
%f(default), the resultstris a single string representing the whole input matrix. Otherwise,strhas as many elements as the input matrixa.- isWrapped
is a boolean to indicate if the result must be wrapped inside technical delimiters. The default value is %T (true). The delimiters depend on the export format. It is
- '$' for latex and tex
- nothing for mathml
for HTML:
- nothing if
processByElementis%T; - or the opening tag
<table valign="middle" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" ..>otherwise. Note that the "</table>" closure is then always included, even ifisWrappedis%F. This allows to fully customize the table style and attributes, instead of using the default ones.
- nothing if
- str
a single string (if
processByElementis %F), or a matrix of strings otherwise (with size(str)==size(a)): the representation of the input objecta.
Description
prettyprint() provides a formatted representation of a Scilab object.
The format can be TeX, LaTeX, MathML, or HTML.
The result can be used in third party applications, or within Scilab: Almost all graphic functions requiring or accepting some text input support it as LaTeX expressions (see Scilab graphic features).
In addition, some GUI features accept and render HTML inputs. The special export format 'html4' must be used to display linear dynamical systems in a Scilab GUI like messagebox().
 | When an array of cells includes some matrices or other arrays, the same chosen delimiters
are used for the cells array and for its elements that are also arrays. |
 | The output format of all decimal numbers included in the input object is driven by the
|
Rendering some MathML or/and LaTeX codes in a HTML page:
Only the Firefox web browser supports natively the <math> MathML tag, that can embed some mathML code, and renders it.
To render MathML code in any web browser,
- put the following HTML instruction only once before the first use of
<math>: <script src='https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/mathjax/2.7.5/MathJax.js?config=TeX-MML-AM_CHTML' async/>. This is typically done in the<head>..</head>section of the HTML page. - put every set of MathML instructions between
<math>..</math>.
 | The same Hence, the HTML code of a page can mix some LaTeX and MathML instructions that will be parsed and rendered accordingly. |
Please see examples provided in the dedicated section below.
Examples
str = prettyprint(rand(3,3)) // Return the LaTeX representation of a 3,3 matrix xstring(0.2,0.2,str) // Show the representation in a graphic Windows prettyprint(rand(3,4),"mathml") // Return the MathML representation of a 3,4 matrix prettyprint(rand(3,4),"mathml","[") // Return the MathML representation of a 3,4 matrix with '[' as delimiter s=poly(0,'s'); G=[1,s;1+s^2,3*s^3]; xstring(0.2,0.2,prettyprint(G*s-1)); // Show a polynomial through a LaTeX representation
Set of objects to be defined before using them in all next examples:
bool = [ %t %t ; %f %t ] i16 = int16([ 26595 1212 4257 -4466 9784 -4226 3404 5743 3 10032 30471 6 14918 267 30 ]) num = [-123.45, %inf, 5.427e-123 %nan , 0 , -%inf ] cx = [complex(1,%nan), complex(-1.25d-12, 2) complex(%inf,6.1e167), complex(1,-%inf)] p = [[0*%z ; %z], (%i-%z).^[1 3;2 4]]; string(p) text = ["André''s got 50% of 1430 $, & the ""remainder"" 1 month later." "x=A\B is such that A*x=B, with A in {a<b, 1-a, ~a, ^a}. _#"] ce = {["a b"; "cdefg"], %t, %z./[%z-1, %z^2+1] ; (1-%s)^3, %pi, int8(rand(2,3)*200)} A = grand(3,3,"uin",-999,999)/100; B = grand(3,2,"uin",-999,999)/100; C = grand(2,3,"uin",-999,999)/100; linsys = syslin("c", A, B, C); L = list("Booleans:", bool, "int16:", i16, "Decimal numbers:", num, .. "Complex numbers:", cx, "Polynomials:", p, "Text:", text, .. "Cells array, embedding rationals:", ce, "Linear dynamical system:");
--> bool = [ %t %t; %f %t ];
bool =
T T
F T
--> i16 = int16([
> 26595 1212 4257 -4466 9784
> -4226 3404 5743 3 10032
> 30471 6 14918 267 30 ])
i16 =
26595 1212 4257 -4466 9784
-4226 3404 5743 3 10032
30471 6 14918 267 30
--> num = [-123.45, %inf, 5.427e-123
> %nan , 0 , -%inf ]
num =
-123.45 Inf 0.
Nan 0. -Inf
--> cx = [complex(1,%nan), complex(-1.25d-12, 2)
> complex(%inf,6.1e167), complex(1,-%inf)]
cx =
1. + Nani -1.250D-12 + 2.i
Inf + 6.10D+167i 1. - Infi
--> p = [[0*%z ; %z], (%i-%z).^[1 3;2 4]]; string(p)
ans =
! 2 3 !
!0 i - z - i + 3z + 3iz - z !
! !
! 2 2 3 4 !
!z - 1 - 2iz + z 1 + 4iz - 6z - 4iz + z !
--> text = ["André''s got 50% of 1430 $, & the ""remainder"" 1 month later."
> "x=A\B is such that A*x=B, with A in {a<b, 1-a, ~a, ^a}. _#"]
text =
!André's got 50% of 1430 $, & the "remainder" 1 month later. !
!x=A\B is such that A*x=B, with A in {a<b, 1-a, ~a, ^a}. _# !
--> ce = makecell([2 3],["a b"; "cdefg"], %t, %z./[%z-1, %z^2+1], ..
(1-%s)^3, %pi, int8(rand(2,3)*200))
ce =
[2x1 string ] [1x1 boolean ] [ r ]
[1x1 polynomial] [1x1 constant] [2x3 int8]
Export to LaTeX format:
// Please run the first example section to define objects to be converted, // before executing this section. prettyprint(bool, "latex") prettyprint(i16, "latex") prettyprint(num, "latex") prettyprint(cx, "latex") prettyprint(p, "latex") prettyprint(text, "latex") prettyprint(ce, "latex") prettyprint(linsys, "latex", "")
--> prettyprint(bool, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}T&T\cr F&T\cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(i16, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}26595&1212&4257&-4466&9784\cr -4226&3404&5743&3&10032\cr 3047
1&6&14918&267&30\cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(num, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}-123.45&{\infty}&5.43\!\times\!10^{-123}\cr {\mathrm{NaN}}&0&
{-\infty}\cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(cx, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}1+{\mathrm{NaN}}i&-1.250\!\times\!10^{-12}+2i\cr {\infty}+6.1
0\!\times\!10^{167}i&1{-\infty}i\cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(p, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}0z&i-z &-i+3z +3iz^{2} -z^{3} \cr z &-1-2iz +z^{2} &1+4iz -6z
^{2} -4iz^{3} +z^{4} \cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(text, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}\mathsf{\text{André's got 50\% of 1430 \$, \& the "remainder"
1 month later.}}\cr \mathsf{\text{x=A\backslash\!B is such that A*x=B, with A
in \{a\!<\!b, 1-a, \sim\!a, \^\;\,a\}. _#}}\cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(ce, "latex")
ans =
${\begin{pmatrix}{\begin{pmatrix}\mathsf{\text{a b}}\cr \mathsf{\text{cdefg}}\
cr \end{pmatrix}}&T&{\begin{pmatrix}{\frac{z }{-1+z }}&{\frac{z }{1+z^{2} }}\c
r \end{pmatrix}}\cr 1-3s +3s^{2} -s^{3} &3.1415927&{\begin{pmatrix}51&23&-121\
cr 125&122&66\cr \end{pmatrix}}\cr \end{pmatrix}}$
--> prettyprint(linsys, "latex", "")
ans =
${\begin{matrix}{\left\{\begin{array}{rcl}\dot{X}(t)&=&{\begin{pmatrix}9.35&-5
.94&-1.21\cr 6.65&-6.92&2.83\cr 2.49&2.7&0.34\cr \end{pmatrix}} X(t)+{\begin{p
matrix}-0.11&-8.3\cr 1.84&7.45\cr -4.93&-1.35\cr \end{pmatrix}}U(t)\cr Y(t) &=
& {\begin{pmatrix}5.45&5.61&0.94\cr -5.82&5.41&0.14\cr \end{pmatrix}} X(t) \en
d{array}\right.}\cr \end{matrix}}$
Export to LaTeX and rendering in a graphic figure:
// Please run the first example section to define objects to be converted, // before executing this section. y = 1.; clf gcf().axes_size = [500 670]; gca().margins = 0.01*[1 1 1 1]; for obj = L if type(obj)<>10 | part(obj,$)<>":" obj = prettyprint(obj, "latex"); end r = stringbox(obj, 0, 0); y = y - strange(r(2,:))-0.015; xstring(0.1, y, obj); end obj = prettyprint(linsys,"latex","") y = y - strange(stringbox(obj, 0, 0)(2,:))-0.02; xstring(0.1, y, obj); set(gca().children, "fractional_font","on", "font_size",2.5);
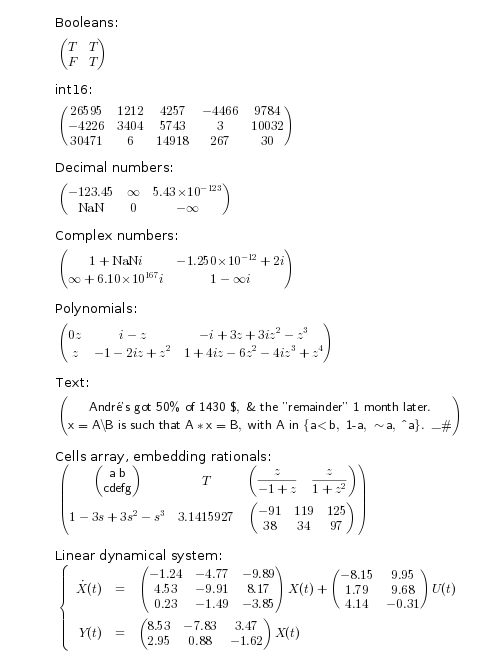
Export to LaTeX and rendering in a HTML.5 page for any web browser, using MathJax:
// Please run the first example section to define objects to be converted, // before executing this section. // // Header: mathjaxURL = "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/mathjax/2.7.5/MathJax.js?config=TeX-MML-AM_CHTML" html = ["<!doctype html>" "<html>" "<meta http-equiv=""Content-Type"" content=""text/html;charset=UTF-8"">" "<script src=''" + mathjaxURL + "'' async></script>" "<!-- then any LaTeX expression delimited with \[ .. \] will be rendered -->" "<body>" ]; // List of objects: for obj = L if type(obj)<>10 | part(obj,$)<>":" obj = prettyprint(obj, "latex", "(", %f, %f); html = [html ; "\[ "+ obj + "\]" ; "<br/>"]; else html = [html ; obj + " <br/>"]; end end html = [html ; "\[ "+ prettyprint(linsys, "latex", "") + "\]<br/><br/>"]; // Footer: html = [html ; "</body>" ; "</html>"]; File = TMPDIR + filesep() + "prettyprint_mathjax.html" mputl(html, File); edit(File) // See the HTML code winopen(File) // Display the page in your browser
Please note that for string input, the protection needed for some special LaTeX characters is displayed as is by MathJax:

MathML: Exporting Scilab objects into MathML, and rendering them in a HTML page using the <math> tag. We still use MathJax to render the code in any web browser:
// Please run the first example section to define objects to be converted, // before executing this section. // // Header: mathjaxURL = "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/mathjax/2.7.5/MathJax.js?config=TeX-MML-AM_CHTML" html = ["<!doctype html>" "<html>" "<head>" "<meta http-equiv=""Content-Type"" content=""text/html;charset=UTF-8"">" "<script src=''" + mathjaxURL + "'' async></script>" "<!-- then any MathML expression embedded in <math>..</math> will be rendered -->" "</head>" "<body>" ]; // List of objects: for obj = L if type(obj)<>10 | part(obj,$)<>":" obj = prettyprint(obj, "mathml", "(", %f, %f); html = [html ; "<math>" ; obj ; "</math><br/><br/>"]; else html = [html ; obj + " <br/>"]; end end html = [html ; "<math>" ; prettyprint(linsys, "mathml", "") ; "</math>"]; // Footer: html = [html ; "</body>" ; "</html>"]; File = TMPDIR + filesep() + "prettyprint_mathML.html" mputl(html, File); editor(File) // See the HTML and MathML code winopen(File) // Render the page in your browser

Export in HTML(4) for rendering in messagebox(): Only the "|" or "||" delimiters can be used (or "" for no delimiter"). In addition, "_" is used in HTML mode to get any table with borders:
// Please run the first example section to define objects to be converted, // before executing this section. // // Header: html = ["<!doctype html>" "<html>" "<meta http-equiv=""Content-Type"" content=""text/html;charset=UTF-8"">" "<body>" ]; // List of objects: for obj = L if type(obj)<>10 | part(obj,$)<>":" obj = prettyprint(obj, "html", "|"); html = [html ; obj ; "<br/><br/>"]; else html = [html ; obj + " <br/>"]; end end html = [html ; prettyprint(linsys, "html", "|4")]; // Footer: html = [html ; "</body>" ; "</html>"]; File = TMPDIR + filesep() + "prettyprint_HTML.html" mputl(html, File); edit(File) // See the HTML code winopen(File) // Display the page in your browser messagebox(html, "prettyprint() test => messagebox(HTML.4)");
Rendering in a messagebox():

Still in HTML, using "_" to get table borders:
// Please run the first example section to define i16, before executing this section. messagebox(["The table is:" ; "<br>" ; prettyprint(i16,"html","_")])
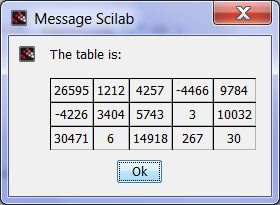
See also
- MathJax
- MathML namespace
- math_rendering_features_in_graphic — Affiche les équations mathématiques dans le graphique Scilab grâce à MathML ou LaTeX.
- format — configure le format par défaut d'affichage des nombres décimaux
- xnumb — dessine des nombres
- string — conversion en chaîne de caractères
- pol2str — conversion polynôme => texte
- msprintf — converts, formats, and writes data in a string
- uicontrol(table) — create a Graphic User Interface object
- sci2exp — returns a string able to generate a given Scilab object
History
| Version | Description |
| 5.2.0 | Function introduced. |
| 6.1.0 | Export to HTML added. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << part | Chaînes de caractères | regexp >> |