- Scilab Help
- CACSD (Computer Aided Control Systems Design)
- Formal representations and conversions
- Plot and display
- abinv
- arhnk
- arl2
- arma
- arma2p
- arma2ss
- armac
- armax
- armax1
- arsimul
- augment
- balreal
- bilin
- bstap
- cainv
- calfrq
- canon
- ccontrg
- cls2dls
- colinout
- colregul
- cont_mat
- contr
- contrss
- copfac
- csim
- ctr_gram
- damp
- dcf
- ddp
- dhinf
- dhnorm
- dscr
- dsimul
- dt_ility
- dtsi
- equil
- equil1
- feedback
- findABCD
- findAC
- findBD
- findBDK
- findR
- findx0BD
- flts
- fourplan
- freq
- freson
- fspec
- fspecg
- fstabst
- g_margin
- gamitg
- gcare
- gfare
- gfrancis
- gtild
- h2norm
- h_cl
- h_inf
- h_inf_st
- h_norm
- hankelsv
- hinf
- imrep2ss
- inistate
- invsyslin
- kpure
- krac2
- lcf
- leqr
- lft
- lin
- linf
- linfn
- linmeq
- lqe
- lqg
- lqg2stan
- lqg_ltr
- lqr
- ltitr
- macglov
- minreal
- minss
- mucomp
- narsimul
- nehari
- noisegen
- nyquistfrequencybounds
- obs_gram
- obscont
- observer
- obsv_mat
- obsvss
- p_margin
- parrot
- pfss
- phasemag
- plzr
- pol2des
- ppol
- prbs_a
- projsl
- repfreq
- ric_desc
- ricc
- riccati
- routh_t
- rowinout
- rowregul
- rtitr
- sensi
- sident
- sorder
- specfact
- ssprint
- st_ility
- stabil
- sysfact
- syslin
- syssize
- time_id
- trzeros
- ui_observer
- unobs
- zeropen
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
lqg
LQG compensator
Calling Sequence
[K]=lqg(P,r)
Arguments
- P
syslinlist (augmented plant) in state-space form- r
1x2 row vector = (number of measurements, number of inputs) (dimension of the 2,2 part of
P)- K
syslinlist (controller)
Description
lqg computes the linear optimal LQG (H2) controller for the
"augmented" plant P=syslin('c',A,B,C,D) (continuous time) or
P=syslin('d',A,B,C,D) (discrete time).
The function lqg2stan returns P and r given the
nominal plant, weighting terms and variances of noises.
K is given by the following ABCD matrices:
[A+B*Kc+Kf*C+Kf*D*Kc,-Kf,Kc,0] where Kc=lqr(P12)
is the controller gain and Kf=lqe(P21) is the filter gain.
See example in lqg2stan.
Examples
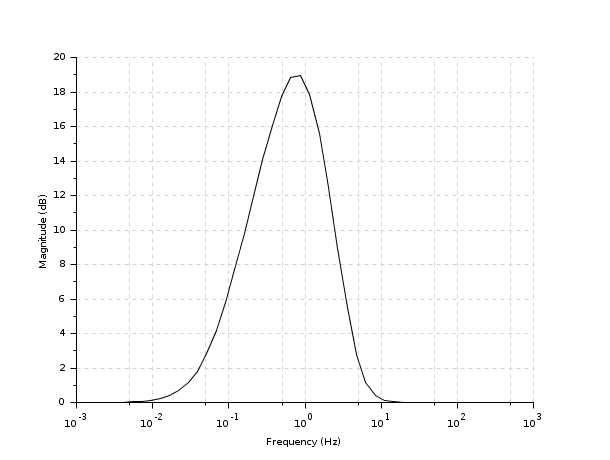
s=poly(0,'s'); Plant=syslin('c',[1/(s+1)*s/(s-1)^2]); //Nominal Plant P22=tf2ss(Plant); //...in state-space form [ny,nu,nx]=size(P22); rand('seed',0);rand('normal'); bigQ=rand(nx+nu,nx+nu); bigQ=bigQ*bigQ'; bigR=rand(nx+ny,nx+ny); bigR=bigR*bigR'; //random weighting matrices [Plqg,r]=lqg2stan(P22,bigQ,bigR); //LQG pb as a standard problem Klqg=lqg(Plqg,r); //Controller spec(h_cl(Plqg,r,Klqg)) //Check internal stability [Slqg,Rlqg,Tlqg]=sensi(P22,Klqg); //Sensitivity functions frq=logspace(-3,3); //10^-3 to 10^3 y=svplot(Slqg); //Computes singular values; gainplot(frq,y) //Plot sing. values
See Also
| Report an issue | ||
| << lqe | CACSD (Computer Aided Control Systems Design) | lqg2stan >> |