- Scilab Online Help
- Signal Processing
- How to
- Signal
- analpf
- bilt
- buttmag
- casc
- cepstrum
- cheb1mag
- cheb2mag
- chepol
- convol
- corr
- cspect
- czt
- detrend
- dft
- ell1mag
- eqfir
- eqiir
- faurre
- ffilt
- fft
- fft2
- fftshift
- filt_sinc
- filter
- find_freq
- findm
- frfit
- frmag
- fsfirlin
- group
- hank
- hilb
- hilbert
- iir
- iirgroup
- iirlp
- intdec
- jmat
- kalm
- lattn
- lattp
- lev
- levin
- lindquist
- mese
- mfft
- mrfit
- %asn
- %k
- %sn
- phc
- pspect
- remez
- remezb
- rpem
- sincd
- srfaur
- srkf
- sskf
- syredi
- system
- trans
- wfir
- wiener
- wigner
- window
- yulewalk
- zpbutt
- zpch1
- zpch2
- zpell
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
cspect
two sided cross-spectral estimate between 2 discrete time signals using the correlation method
Calling Sequence
[sm [,cwp]]=cspect(nlags,npoints,wtype,x [,y] [,wpar]) [sm [,cwp]]=cspect(nlags,npoints,wtype,nx [,ny] [,wpar])
Arguments
- x
vector, the data of the first signal.
- y
vector, the data of the second signal. If
yis omitted it is supposed to be equal tox(auto-correlation). If it is present, it must have the same numer of element thanx.- nx
a scalar : the number of points in the
xsignal. In this case the segments of the x signal are loaded by a user defined function namedgetx(see below).- ny
a scalar : the number of points in the
ysignal. In this case the segments of theysignal are loaded by a user defined function namedgety(see below). If presentnymust be equal tonx.- nlags
number of correlation lags (positive integer)
- npoints
number of transform points (positive integer)
- wtype
The window type
're': rectangular'tr': triangular'hm': Hamming'hn': Hanning'kr': Kaiser,in this case the wpar argument must be given'ch': Chebyshev, in this case the wpar argument must be given
- wpar
optional parameters for
Kaiser and Chebyshev windows:'kr':
wpar must be a strictly positive number'ch':
wparmust be a 2 element vector[main_lobe_width,side_lobe_height]with0<main_lobe_width<.5, andside_lobe_height>0
- sm
The power spectral estimate in the interval
[0,1]of the normalized frequencies. It is a row array of sizenpoints. The array is real in case of auto-correlation and complex in case of cross-correlation.- cwp
the unspecified Chebyshev window parameter in case of Chebyshev windowing, or an empty matrix.
Description
Computes the cross-spectrum estimate of two signals
x and y if both are given and the
auto-spectral estimate of x otherwise. Spectral
estimate obtained using the correlation method.
The cross spectrum of two signal x and y is defined to be
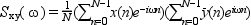
The correlation method calculates the spectral estimate as the Fourier transform of a modified estimate of the auto/cross correlation function. This auto/cross correlation modified estimate consist of repeatedly calculating estimates of the autocorrelation function from overlapping sub-segments if the data, and then averaging these estimates to obtain the result.
The number of points of the window is
2*nlags-1.
For batch processing, thex and
y data may be read segment by segment using the
getxand gety user defined
functions. These functions have the following calling sequence:
xk=getx(ns,offset) and
yk=gety(ns,offset) where ns is the
segment size and offset is the index of the first
element of the segment in the full signal.
Warning
For Scilab version up to 5.0.2 the returned value was the modulus of the current one.
Reference
Oppenheim, A.V., and R.W. Schafer. Discrete-Time Signal Processing, Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1999
Examples
rand('normal');rand('seed',0); x=rand(1:1024-33+1); //make low-pass filter with eqfir nf=33;bedge=[0 .1;.125 .5];des=[1 0];wate=[1 1]; h=eqfir(nf,bedge,des,wate); //filter white data to obtain colored data h1=[h 0*ones(1:max(size(x))-1)]; x1=[x 0*ones(1:max(size(h))-1)]; hf=fft(h1,-1); xf=fft(x1,-1);yf=hf.*xf;y=real(fft(yf,1)); sm=cspect(100,200,'tr',y); smsize=max(size(sm));fr=(1:smsize)/smsize; plot(fr,log(sm))
Authors
C. Bunks INRIA
| << corr | Signal Processing | czt >> |