Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
splin2d
双3次スプラインのグリッド2次元補間
呼び出し手順
C = splin2d(x, y, z) C = splin2d(x, y, z, spline_type)
引数
- x
1行nx列のdouble行列, 補間点のx座標. i=1,2,...,nx-1について, x(i)<x(i+1)であることが必要です.
- y
1行ny列のdouble行列, 補間点のy座標. i=1,2,...,ny-1について, y(i)<y(i+1)であることが必要です.
- z
nx行ny列のdouble行列, 関数値.
- spline_type
1行1列の文字列行列, 計算するスプラインの型. 利用可能な値は, spline_type="not_a_knot"および spline_type="periodic".
- C
双3次パッチの係数. このsplin2dの出力引数はinterp2d関数の入力引数です.
説明
この関数は,点(xi,yj,zij)を補間する,
すなわち,全てのi=1,..,nxおよび
j=1,..,nyについて
s(xi,yj)=zijとなるような,
双3次スプラインまたはサブスプライン
sを計算します.
得られるスプラインはsは
(x,y,C)の組で定義されます.
ただし,C は,
(nx-1)(ny-1)個の双3次パッチの各々の係数
[x(i) x(i+1)]x[y(j) y(j+1)]
を有する
(長さ16(nx-1)(ny-1)の)ベクトルです,
sは次のように定義されます :
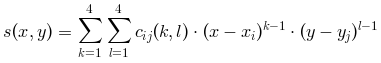
いくつかの点でinterp2d関数により
sの評価を行う必要があります.
適当なspline_typeパラメータを選択することにより,
複数の種類のスプラインを計算することができます.
双3次スプライン(またはサブスプライン)を計算するために使用する方法は,
古い形式の手法,すなわち,
各グリッドの点(xi,yj)において
1階微分ds/dx(xi,yj) および
ds/dy(xi,yj)と相互微分
d2s/dxdy(xi,yj)の近似値を計算する手法です.
これらの微係数は,C2関数
(sは連続2階微分可能)となる
1次元スプライン法の平均,または
C1関数となるローカルな近似法の平均により,計算されます.
この手法は,spline_typeパラメータにより
選択されます.(詳細は,
splinを参照ください) :
- "not_a_knot"
これがデフォルトです.
- "periodic"
基本関数に周期性がある場合に使用します: [1,ny]の範囲のあらゆるjについてz(1,j) = z(nx,j), [1,nx]の範囲のあらゆるuについてz(i,1) = z(i,ny) となる必要がありますが,これはインターフェイスでは検証されません.
注意
精度の観点から,not_a_knot型,また 基本となる補間関数に周期性がある場合にはperiodic型を使用してください.
natural, monotone, fast (または fast_periodic) 型は, 例えば発振を防止したい場合(monotone がこの用途には最も強力です)に有用です.
より簡便な方法で双三次パッチの係数を得るには,
c = matrix(C, [4,4,nx-1,ny-1])を使用し,
続いてパッチ(i,j)(前記の式参照)
の係数(k,l)
をc(k,l,i,j)に保存します.
ただし,interp2d関数は,
ハイパー行列cではなく,
大きなベクトルCを引数として受け入れます
(C=c(:)とすることでcから
容易にCを取得できます).
例
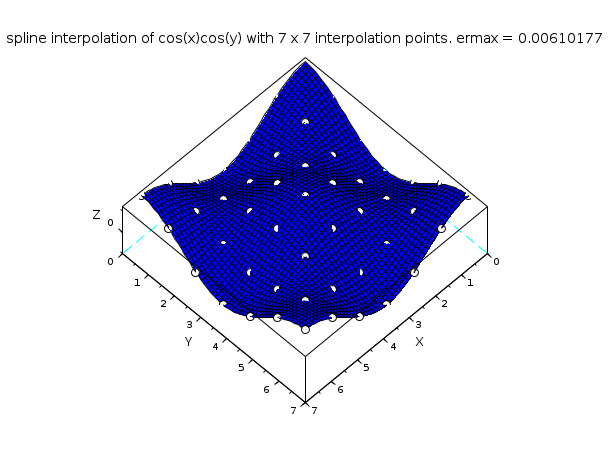
// 例1 : cos(x)cos(y)の補間 n = 7; // n x n 個の補間点を有する通常のグリッドを // 使用します x = linspace(0,2*%pi,n); y = x; z = cos(x')*cos(y); C = splin2d(x, y, z, "periodic"); m = 50; // 評価グリッドの離散化パラメータ xx = linspace(0,2*%pi,m); yy = xx; [XX,YY] = ndgrid(xx,yy); zz = interp2d(XX,YY, x, y, C); emax = max(abs(zz - cos(xx')*cos(yy))); clf() plot3d(xx, yy, zz, flag=[2 4 4]) [X,Y] = ndgrid(x,y); param3d1(X,Y,list(z,-9*ones(1,n)), flag=[0 0]) str = msprintf(" with %d x %d interpolation points. ermax = %g",n,n,emax) xtitle("spline interpolation of cos(x)cos(y)"+str)
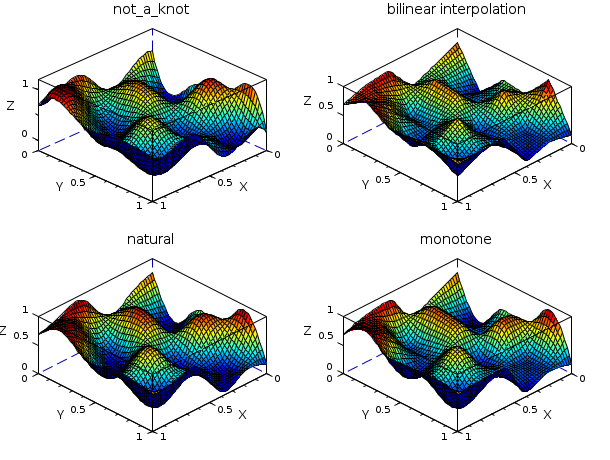
// 例2 : ランダムなデータに異なる補間関数を適用 n = 6; x = linspace(0,1,n); y = x; z = rand(n,n); np = 50; xp = linspace(0,1,np); yp = xp; [XP, YP] = ndgrid(xp,yp); ZP1 = interp2d(XP, YP, x, y, splin2d(x, y, z, "not_a_knot")); ZP2 = linear_interpn(XP, YP, x, y, z); ZP3 = interp2d(XP, YP, x, y, splin2d(x, y, z, "natural")); ZP4 = interp2d(XP, YP, x, y, splin2d(x, y, z, "monotone")); gcf().color_map = jetcolormap(64); clf() subplot(2,2,1) plot3d1(xp, yp, ZP1, flag=[2 2 4]) xtitle("not_a_knot") subplot(2,2,2) plot3d1(xp, yp, ZP2, flag=[2 2 4]) xtitle("bilinear interpolation") subplot(2,2,3) plot3d1(xp, yp, ZP3, flag=[2 2 4]) xtitle("natural") subplot(2,2,4) plot3d1(xp, yp, ZP4, flag=[2 2 4]) xtitle("monotone")
// 例3 : ステップ関数のnot_a_knot スプラインおよびmonotoneスプライン // a = 0; b = 1; c = 0.25; d = 0.75; // 補間グリッドを作成 n = 11; x = linspace(a,b,n); ind = find(c <= x & x <= d); z = zeros(n,n); z(ind,ind) = 1; // 正方形の中にステップ // 評価グリッドを作成 np = 220; xp = linspace(a,b, np); [XP, YP] = ndgrid(xp, xp); zp1 = interp2d(XP, YP, x, x, splin2d(x,x,z)); zp2 = interp2d(XP, YP, x, x, splin2d(x,x,z,"monotone")); // プロット clf() gcf().color_map = jetcolormap(128); subplot(1,2,1) plot3d1(xp, xp, zp1, flag=[-2 6 4]) xtitle("spline (not_a_knot)") subplot(1,2,2) plot3d1(xp, xp, zp2, flag=[-2 6 4]) xtitle("subspline (monotone)")
参照
- cshep2d — 2次元3次シェパード(散布)補間
- linear_interpn — n 次元線形補間
- interp2d — 双3次スプライン (2d) 評価関数
| Report an issue | ||
| << splin | Interpolation | splin3d >> |