- Scilab help
- CACSD
- abcd
- abinv
- arhnk
- arl2
- arma
- arma2p
- armac
- armax
- armax1
- arsimul
- augment
- balreal
- bilin
- black
- bode
- bstap
- cainv
- calfrq
- canon
- ccontrg
- chart
- cls2dls
- colinout
- colregul
- cont_frm
- cont_mat
- contr
- contrss
- copfac
- csim
- ctr_gram
- dbphi
- dcf
- ddp
- des2ss
- des2tf
- dhinf
- dhnorm
- dscr
- dsimul
- dt_ility
- dtsi
- equil
- equil1
- evans
- feedback
- findABCD
- findAC
- findBD
- findBDK
- findR
- findx0BD
- flts
- fourplan
- frep2tf
- freq
- freson
- fspecg
- fstabst
- g_margin
- gainplot
- gamitg
- gcare
- gfare
- gfrancis
- gtild
- h2norm
- h_cl
- h_inf
- h_inf_st
- h_norm
- hallchart
- hankelsv
- hinf
- imrep2ss
- inistate
- invsyslin
- kpure
- krac2
- lcf
- leqr
- lft
- lin
- linf
- linfn
- linmeq
- lqe
- lqg
- lqg2stan
- lqg_ltr
- lqr
- ltitr
- m_circle
- macglov
- markp2ss
- minreal
- minss
- mucomp
- narsimul
- nehari
- nicholschart
- noisegen
- nyquist
- obs_gram
- obscont
- observer
- obsv_mat
- obsvss
- p_margin
- parrot
- pfss
- phasemag
- ppol
- prbs_a
- projsl
- reglin
- repfreq
- ric_desc
- ricc
- riccati
- routh_t
- rowinout
- rowregul
- rtitr
- sensi
- sgrid
- show_margins
- sident
- sm2des
- sm2ss
- sorder
- specfact
- ss2des
- ss2ss
- ss2tf
- st_ility
- stabil
- svplot
- sysfact
- syssize
- tf2des
- tf2ss
- time_id
- trzeros
- ui_observer
- unobs
- zeropen
- zgrid
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
black
Black-Nichols diagram of a linear dynamical system
Calling Sequence
black( sl,[fmin,fmax] [,step] [,comments] ) black( sl,frq [,comments] ) black(frq,db,phi [,comments]) black(frq,repf [,comments])
Arguments
- sl
a continuous or discrete time SIMO linear dynamical system ( see: syslin).
- fmin,fmax
real scalars (frequency bounds)
- frq
row vector or matrix (frequencies)
- db,phi
row vectors or matrices (modulus, phase)
- repf
row vectors or matrices (complex frequency response)
- step
real
- comments
string
Description
Black's diagram (Nichols'chart) for a linear system ( see: syslin). sl can be a continuous-time or
discrete-time SIMO system. In case of
multi-output the outputs are plotted with different colors.
The frequencies are given by the bounds
fmin,fmax (in Hz) or by a row-vector
(or a matrix for multi-output) frq.
step is the ( logarithmic ) discretization step.
(see calfrq for the choice of default value).
comments is a vector of character strings
(captions).
db,phi are the matrices of modulus (in Db) and
phases (in degrees). (One row for each response).
repf matrix of complex numbers. One row for each
response.
To plot the grid of iso-gain and iso-phase of
y/(1+y) use nicolschart().
Default values for fmin and
fmax are 1.d-3,
1.d+3 if sl is continuous-time or
1.d-3, 0.5/sl.dt (nyquist frequency)
if sl is discrete-time.
Examples
//Black diagram s=poly(0,'s'); sl=syslin('c',5*(1+s)/(.1*s^4+s^3+15*s^2+3*s+1)) clf();black(sl,0.01,10);
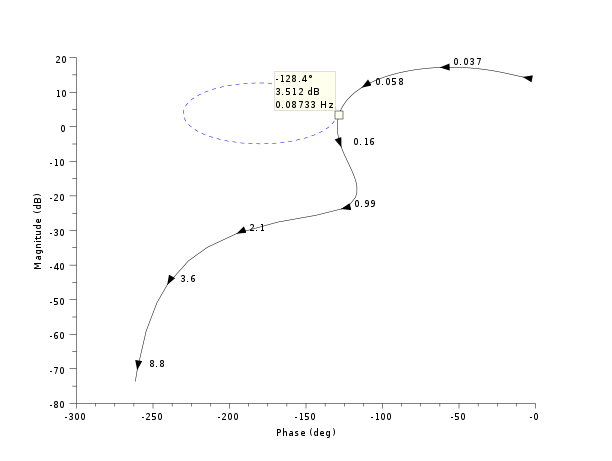
//Black diagram with Nichols chart as a grid s=poly(0,'s'); Plant=syslin('c',16000/((s+1)*(s+10)*(s+100))); //two degree of freedom PID tau=0.2;xsi=1.2; PID=syslin('c',(1/(2*xsi*tau*s))*(1+2*xsi*tau*s+tau^2*s^2)); clf(); black([Plant;Plant*PID ],0.01,100,["Plant";"Plant and PID corrector"]); //move the caption in the lower rigth corner ax=gca();Leg=ax.children(1); Leg.legend_location="in_lower_right"; nicholschart(colors=color('light gray')*[1 1])
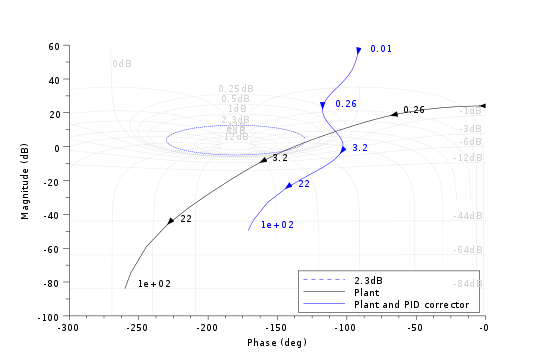
See Also
| << bilin | CACSD | bode >> |