lqi
Linear quadratic integral compensator (full state)
Syntax
[K, X] = lqi(P, Q, R) [K, X] = lqi(P, Q, R, S)
Arguments
- P
The plant state space representation (see syslin) with nx states, nu inputs and ny outputs.
- Q
Real nx+ny by nx+ny symmetric matrix,
- R
full rank nu by nu real symmetric matrix
- S
real nx+ny by nu matrix, the default value is zeros(nx+ny,nu)
- K
a real matrix, the optimal gain
- X
a real symmetric matrix, the stabilizing solution of the Riccati equation
Description
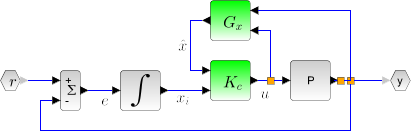
This function computes the linear quadratic integral full-state gain K for the plant P. The associated system block diagram is:
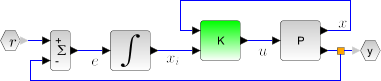
The plant P is given by its state space representation
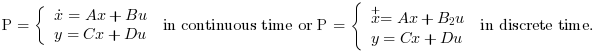
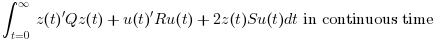
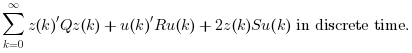
![z=\left[\begin{array}{l}x\\x_i \end{array}\right]](/docs/2023.1.0/pt_BR/_LaTeX_lqi.xml_4.png) and xi is the integrator(s) state(s);
and xi is the integrator(s) state(s);
 | It is assumed that matrix R is non singular. |
 | If the full state of the system is not available, an estimator of the plant state
can be built using the lqe() function. |
Examples
Linear quadratic integral controller of a simplified disk drive using state observer.
//Disk drive model G=syslin("c",[0,32;-31.25,-0.4],[0;2.236068],[0.0698771,0]); t=linspace(0,20,2000); y=csim("step",t,G); //State estimator Wy=1; Wu=1; S=0; Q=G.B*Wu*G.B'; R=Wy+G.D*S + S'*G.D+G.D*Wu*G.D'; S=G.B*Wu*G.D'+S; //State estimator [Kf,X]=lqe(G,Q,R,S); Gx=observer(G,Kf); //LQI compensator wy=100; Q= wy*blockdiag(G.C'*G.C,1); R=1/wy; Kc=lqi(G,Q,R); //full controller K=lft([1;1]*(-Kc(1:2)*Gx(:,[2 1])+Kc(3)*[1/%s 0]),1);//e-->u //Full system H=(-K*G)/.(1);// full system transfer function y=csim("step",t,H); clf;plot(t,y)
See Also
History
| Versão | Descrição |
| 6.0 | lqi() function introduced. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << lqg_ltr | Linear Quadratic | lqr >> |
![\left\lbrace \begin{array}{l}\left[\begin{array}{l}\dot{x}\\ \dot{x_i} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ll}A&0\\-C&0 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l}x\\x_i \end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{l}B\\-G \end{array}\right] u \end{array}\right. \text{ in continuous time }](/docs/2023.1.0/pt_BR/_LaTeX_lqi.xml_5.png)
![\text{P}=\left\lbrace\begin{array}{l}\left[\begin{array}{l}\overset{+}{x}\\ \overset{+}{x_i} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ll}A&0\\-C dt&I \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l}x\\x_i \end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{l}B\\-G dt \end{array}\right] u \end{array} \right.\text{ in discrete time }](/docs/2023.1.0/pt_BR/_LaTeX_lqi.xml_6.png)