cdfnor
累積分布関数: 正規分布
呼び出し手順
[P,Q]=cdfnor("PQ",X,Mean,Std) X=cdfnor("X",Mean,Std,P,Q) Mean=cdfnor("Mean",Std,P,Q,X) Std=cdfnor("Std",P,Q,X,Mean)
パラメータ
- P,Q,X,Mean,Std
同じ大きさの実数ベクトル.
- P,Q (Q=1-P)
正規密度の-infinity からXまでの積分. 入力範囲: (0,1].
- X
正規密度の積分の上限. 入力範囲: ( -infinity, +infinity)
- Mean
正規密度の平均. 入力範囲: (-infinity, +infinity)
- Sd
正規密度の標準偏差. 入力範囲: (0, +infinity).
説明
正規分布のパラメータの一つをそれ以外のパラメータの値を 指定して計算します.
Cody, W.D. (1993). "ALGORITHM 715: SPECFUN - A Portabel FORTRAN Package of Special Function Routines and Test Drivers" acm Transactions on Mathematical Software. 19, 22-32 に基づくANORMを若干修正したものが累積標準正規分布を計算する際に使用されます.
Kennedy and Gentle,Statistical Computing, Marcel Dekker, NY, 1980 のページ90-95に基づく有理関数が,逆標準正規分布を計算する際の ニュートン反復の初期値として使用されます. このため,パラメータに関する探索は不要です.
X < -15の場合, 逆標準正規分布を求める際の初期値として 正規分布の級数展開が使用されます. これは, 26.2.12 of Abramowitz and Stegunの 26.2.12 式によります.
正規分布密度は, exp( - 0.5 * (( X - MEAN)/SD)**2) に比例します.
DCDFLIBから: 累積分布関数, 逆, および他のパラメータ用のFortranルーチンの ライブラリ(February, 1994) Barry W. Brown, James Lovato and Kathy Russell. The University of Texas.
例
// xからpを計算 x = -1; Mean = 0; Std = 1; // P = 0.1586553, Q = 0.8413447 [P,Q]=cdfnor("PQ",x,Mean,Std)
// 非常にまれなxからpを計算 // Pが1に近い場合、Qを使用する必要があり, // Qが1に近い場合, Pを使用する必要があることに注意してください. x = 10; Mean = 0; Std = 1; // P = 1, Q = 7.620D-24 [P,Q]=cdfnor("PQ",x,Mean,Std)
// p,qからxを計算 Mean = 0; Std = 1; p = 0.1; q = 0.9; // x = - 1.2815516 x = cdfnor("X",Mean,Std,p,q)
// p,qから平均を計算 x = 2; Std = 1; p = 0.1; q = 0.9; // 平均 = 3.2815516 Mean = cdfnor("Mean",Std,p,q,x)
// p,qから標準偏差を計算 Mean = 0; p = 0.1; q = 0.9; x = 2; // 標準偏差 = - 1.5606083 Std = cdfnor("Std",p,q,x,Mean)
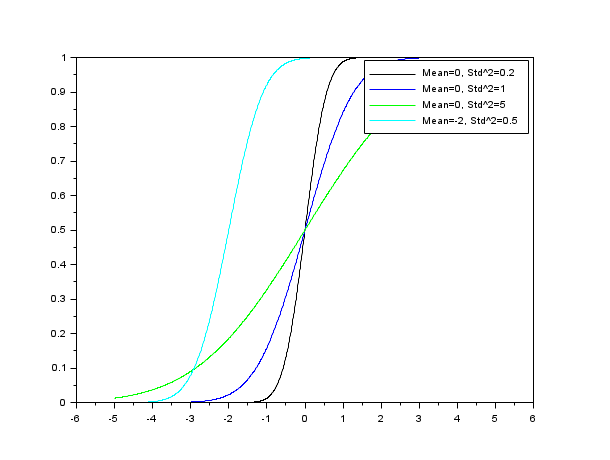
// 関数をプロット h = scf(); Mean = [0 0 0 -2]; Std2 = [0.2 1.0 5.0 0.5]; cols = [1 2 3 4]; nf = size(cols,"*"); lgd = []; for k = 1 : nf x = linspace(-5,5,1000); P=cdfnor("PQ",x,Mean(k)*ones(x),sqrt(Std2(k))*ones(x)); plot(x,P) str = msprintf("Mean=%s, Std^2=%s",string(Mean(k)),string(Std2(k))); lgd($+1) = str; end for k = 1 : nf h.children.children.children(nf - k + 1).foreground = cols(k); end legend(lgd);
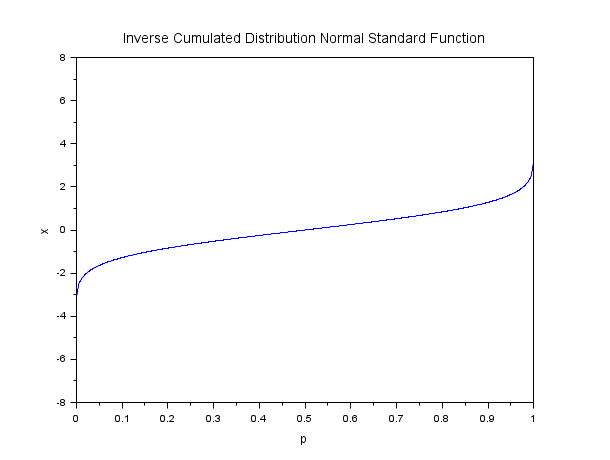
// 逆累積標準関数をプロット Mean = 0; Std = 1; p = linspace(1e-10,1-1e-10,1000); q = 1-p; x = cdfnor("X",Mean*ones(p),Std*ones(p),p,q); plot(p,x) xtitle("Inverse Cumulated Distribution Normal Standard Function","p","x");
// pが0.5に近い時,逆正規CDFは悪条件となります. // これは,p=0.5では,関数値が0にも関わらず1階微分がゼロでなくなるためです. // これにより,関数値に大きな相対誤差が発生し, p が 0.5に近くなれば成る程, // いくつかの桁が不正確となります. Mean = 0; Std = 1; p = 0.500000001; q = 1-p; x = cdfnor("X",Mean,Std,p,q) // 確率の予測値は,式 sqrt(2)*erfinv(2*p-1) に p = 1/2+10^-9 を // 代入して,数式処理ソフトウェアで計算したものです. expected = 2.50662827463100050e-9; // 相対誤差は 1.e-8 であり, 8桁正しいことを意味します. abs(x-expected)/abs(expected)
// ゼロ探索アルゴリズムは何らかの理由で逆が実行できない場合に // 標準偏差を計算できなくなります. Mean = 1; p = 0.5; q = 0.5; x = 1; // 標準偏差 = Nan Std = cdfnor("Std",p,q,x,Mean)
| Report an issue | ||
| << cdfnbn | Cumulated Distribution Functions | cdfpoi >> |