- Scilab Help
- Graphics
- 2d_plot
- LineSpec
- Matplot
- Matplot1
- Matplot properties
- Sfgrayplot
- Sgrayplot
- champ
- champ1
- champ properties
- comet
- contour2d
- contour2di
- contour2dm
- contourf
- errbar
- fchamp
- fec
- fec properties
- fgrayplot
- fplot2d
- grayplot
- grayplot properties
- graypolarplot
- histplot
- paramfplot2d
- plot
- plot2d
- plot2d2
- plot2d3
- plot2d4
- polarplot
- scatter
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
plot
2D plot
Syntax
plot(y,<LineSpec>,<GlobalProperty>) plot(x,y,<LineSpec>,<GlobalProperty>) plot(x1,y1,<LineSpec1>,x2,y2,<LineSpec2>,...xN,yN,<LineSpecN>,<GlobalProperty1>,<GlobalProperty2>,..<GlobalPropertyM>) plot(<axes_handle>,...)
Arguments
- x
a real matrix or vector. If omitted, it is assumed to be the vector
1:nwherenis the number of curve points given by theyparameter.- y
a real matrix or vector.
ycan also be a function defined as a macro or a primitive.- <LineSpec>
This optional argument must be a string that will be used as a shortcut to specify a way of drawing a line. We can have one
LineSpecperyor{x,y}previously entered.LineSpecoptions deals with LineStyle, Marker and Color specifiers (see LineSpec). Those specifiers determine the line style, mark style and color of the plotted lines.- <GlobalProperty>
This optional argument represents a sequence of couple statements
{PropertyName,PropertyValue}that defines global objects' properties applied to all the curves created by this plot. For a complete view of the available properties (see GlobalProperty).- <axes_handle>
This optional argument forces the plot to appear inside the selected axes given by
axes_handlerather than the current axes (see gca).
Description
plot plots a set of 2D curves. plot has been
rebuild to better handle Matlab syntax. To improve graphical
compatibility, Matlab users should use plot (rather than
plot2d).
Data entry specification :
In this paragraph and to be more clear, we won't mention
LineSpec nor GlobalProperty optional arguments
as they do not interfere with entry data (except for "Xdata",
"Ydata" and "Zdata" property, see
GlobalProperty). It is assumed that all those optional
arguments could be present too.
If y is a vector, plot(y) plots vector y
versus vector 1:size(y,'*').
If y is a matrix, plot(y) plots each columns of
y versus vector 1:size(y,1).
If x and y are vectors, plot(x,y) plots
vector y versus vector x. x and
y vectors should have the same number of entries.
If x is a vector and y a matrix plot(x,y)
plots each columns of y versus vector x. In this
case the number of columns of y should be equal to the number
of x entries.
If x and y are matrices, plot(x,y) plots each
columns of y versus corresponding column of x.
In this case the x and y sizes should be the
same.
Finally, if only x or y is a matrix, the
vector is plotted versus the rows or columns of the matrix. The choice is
made depending on whether the vector's row or column dimension matches the
matrix row or column dimension. In case of a square matrix (on
x or y only), priority is given to columns
rather than lines (see examples below).
 | When it is necessary and possible, plot transposes x and y,
to get compatible dimensions; a warning is then issued. For instance,
when x has as many rows as y has columns.
If y is square, it is never transposed. |
y can also be a function defined as a macro or a
primitive. In this case, x data must be given (as a vector or
matrix) and the corresponding computation y(x) is done
implicitly.
The LineSpec and GlobalProperty arguments
should be used to customize the plot. Here is a complete list of the
available options.
- LineSpec
This option may be used to specify, in a short and easy manner, how the curves are drawn. It must always be a string containing references to LineStyle, Marker and Color specifiers.
These references must be set inside the string (order is not important) in an unambiguous way. For example, to specify a red long-dashed line with the diamond mark enabled, you can write :
'r--d'or'--dire'or'--reddiam'or another unambiguous statement... or to be totally complete'diamondred--'(see LineSpec).Note that the line style and color, marks color (and sizes) can also be (re-)set through the polyline entity properties (see polyline_properties).
- GlobalProperty
This option may be used to specify how all the curves are plotted using more option than via
LineSpec. It must always be a couple statement constituted of a string defining thePropertyName, and its associated valuePropertyValue(which can be a string or an integer or... as well depending on the type of thePropertyName). UsingGlobalProperty, you can set multiple properties : every properties available via LineSpec and more : the marker color (foreground and background), the visibility, clipping and thickness of the curves. (see GlobalProperty)Note that all these properties can be (re-)set through the polyline entity properties (see polyline_properties).
Remarks
By default, successive plots are superposed. To clear the previous
plot, use clf(). To enable auto_clear mode as
the default mode, edit your default axes doing:
da=gda();
da.auto_clear = 'on'
For a better display plot function may modify the box property of
its parent Axes. This happens when the parent Axes were created by the call to plot or were empty
before the call. If one of the axis is centered at origin,
the box is disabled.
Otherwise, the box is enabled.
For more information about box property and axis positioning see axes_properties
A default color table is used to color plotted curves if you do not specify a color. When drawing multiple lines, the plot command automatically cycles through this table. Here are the used colors:
R |
G |
B |
| 0. | 0. | 1. |
| 0. | 0.5 | 0. |
| 1. | 0. | 0. |
| 0. | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| 0.75 | 0. | 0.75 |
| 0.75 | 0.75 | 0. |
| 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
Enter the command plot to see a demo.
Examples
// x initialisation x=[0:0.1:2*%pi]'; //simple plot plot(sin(x))
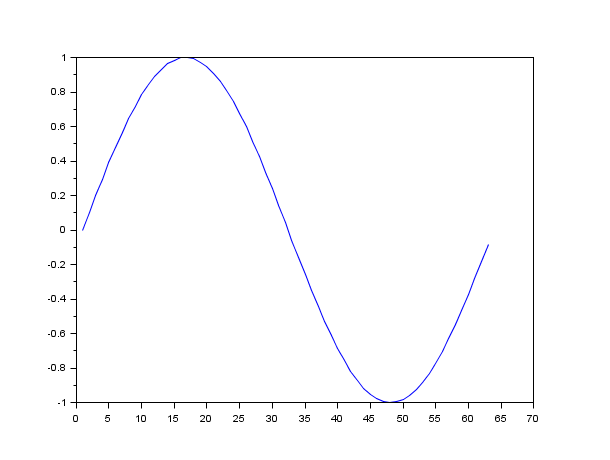
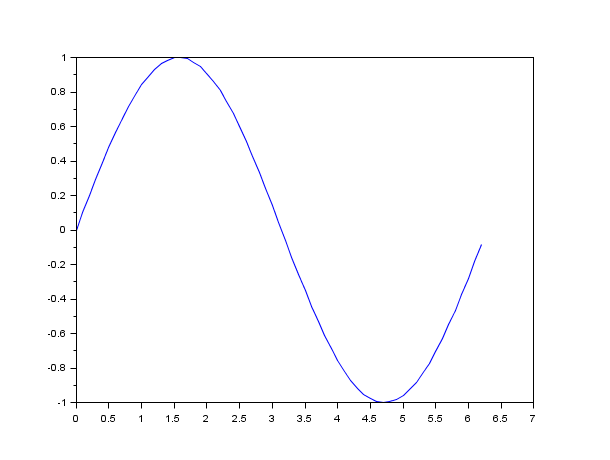
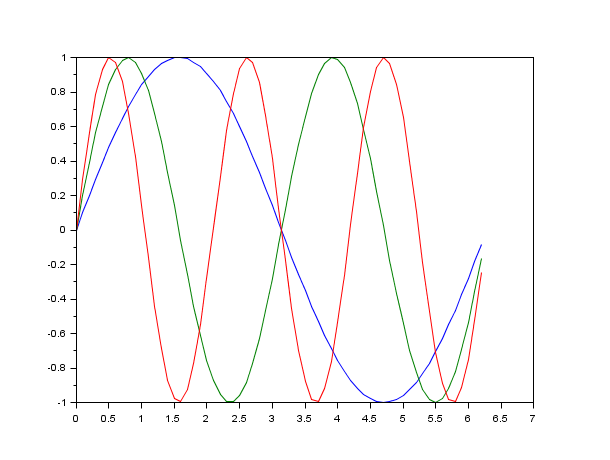
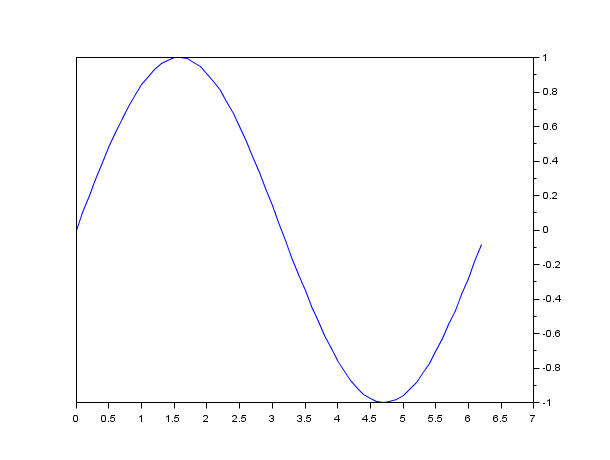
clf() x=[0:0.1:2*%pi]'; // axis on the right plot(x,sin(x)) a=gca(); // Handle on current axes entity a.y_location ="right"; clf()
x=[0:0.1:2*%pi]'; // axis centered at (0,0) plot(x-4,sin(x),x+2,cos(x)) a=gca(); // Handle on axes entity a.x_location = "origin"; a.y_location = "origin"; // Some operations on entities created by plot ... isoview("on"); a.children // list the children of the axes : here it is an Compound child composed of 2 entities poly1= a.children.children(2); //store polyline handle into poly1 poly1.foreground = 4; // another way to change the style... poly1.thickness = 3; // ...and the thickness of a curve. poly1.clip_state='off' // clipping control isoview("off");
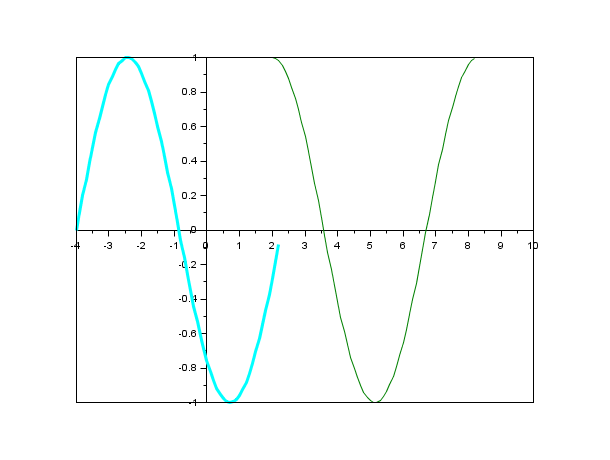
//LineSpec and GlobalProperty examples: clf(); t=0:%pi/20:2*%pi; plot(t,sin(t),'ro-.',t,cos(t),'cya+',t,abs(sin(t)),'--mo') scf(2) plot([t ;t],[sin(t) ;cos(t)],'xdat',[1:2]) scf(3) axfig3 = gca(); scf(4) // should remain blank plot(axfig3,[t ;t],[sin(t) ;cos(t)],'zdat',[1:2],'marker','d','markerfac','green','markeredg','yel') xdel(winsid())
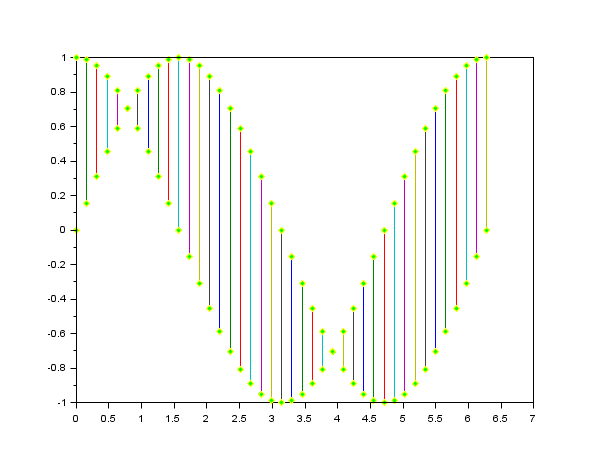
//Data specification t=-%pi:0.1:%pi; size(t) plot(t) // simply plots y versus t vector size
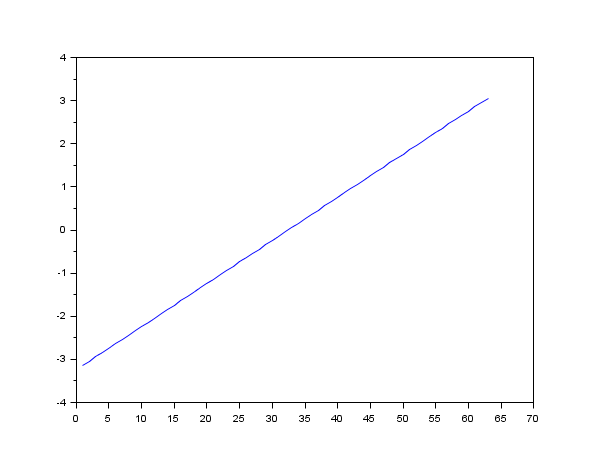
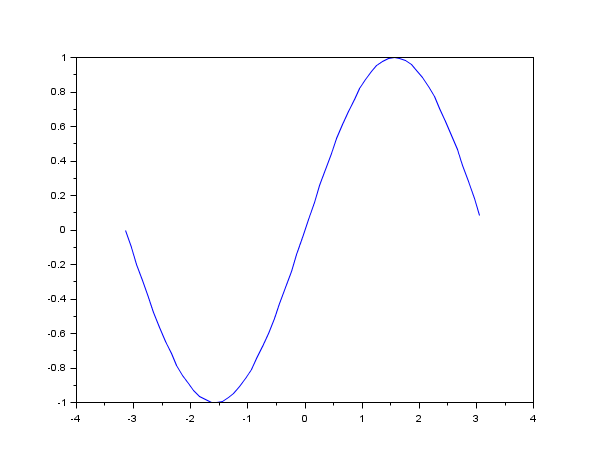
clf(); t=[1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7]; plot(t) // plots each t column versus row size
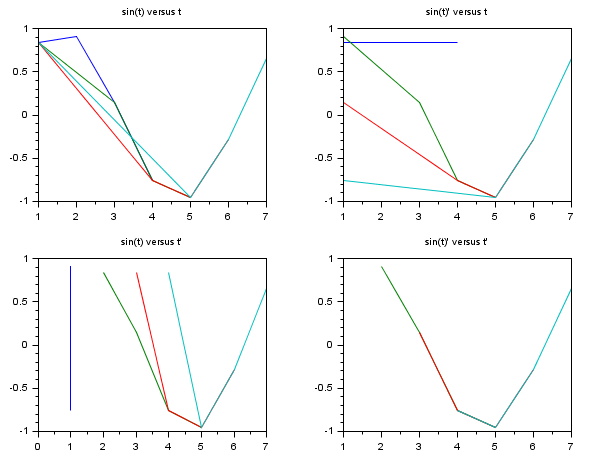
clf(); t=[1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7]; subplot(221) plot(t,sin(t)); // plots sin(t) versus t column by column this time xtitle("sin(t) versus t") subplot(222) plot(t,sin(t)') xtitle("sin(t)'' versus t") subplot(223) plot(t',sin(t)) a=gca(); a.data_bounds=[0 -1;7 1]; // to see the vertical line hidden by the y axis xtitle("sin(t) versus t''") subplot(224) plot(t',sin(t)') xtitle("sin(t)'' versus t''")
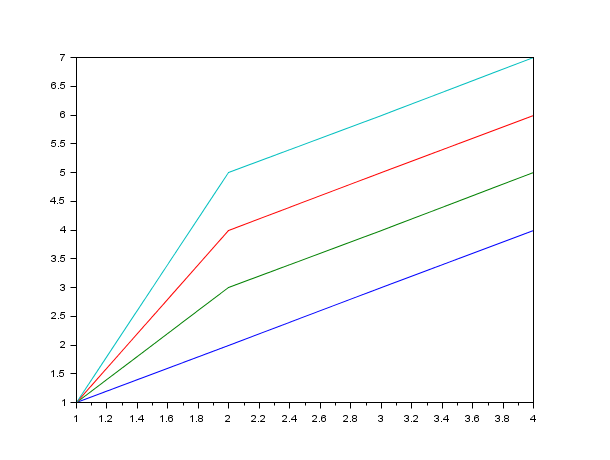
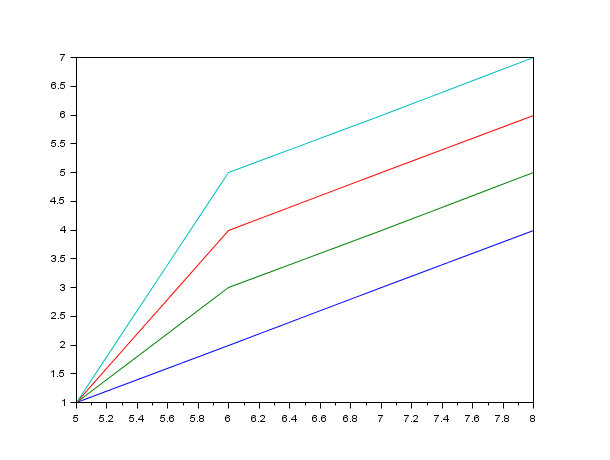
clf(); t=[1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7]; //Special case 1 //x : vector ([5 6 7 8]) and y : matrix (t) x=[5 6 7 8] plot(x,t); plot(x',t); // idem, x is automatically transposed to match t (here the columns)
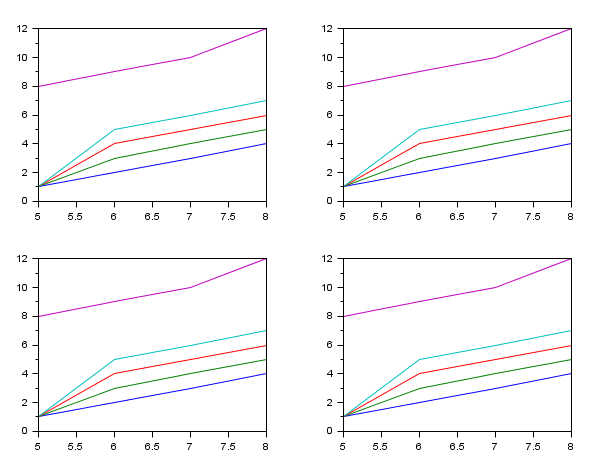
clf() x=[5 6 7 8] t=[1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7]; // Only one matching possibility case: how to make 4 identical plots in 4 manners... // x is 1x4 (vector) and y is 4x5 (non square matrix) subplot(221); plot(x,[t [8;9;10;12]]'); subplot(222); plot(x',[t [8;9;10;12]]); subplot(223); plot(x,[t [8;9;10;12]]'); subplot(224); plot(x',[t [8;9;10;12]]');
clf() t=[1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7]; //Special case 2 // Case where only x or y is a square matrix //x : matrix (t) and y : vector ([1 2 3 4]) plot(t,[1 2 3 4]') // equivalent to plot(t,[1 1 1 1;2 2 2 2;3 3 3 3;4 4 4 4]) plot(t,[1;2;3;4]') // the same plot, but here Y needs to be transposed
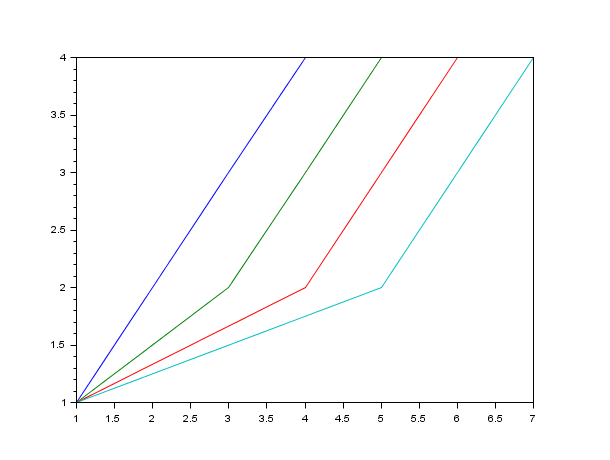
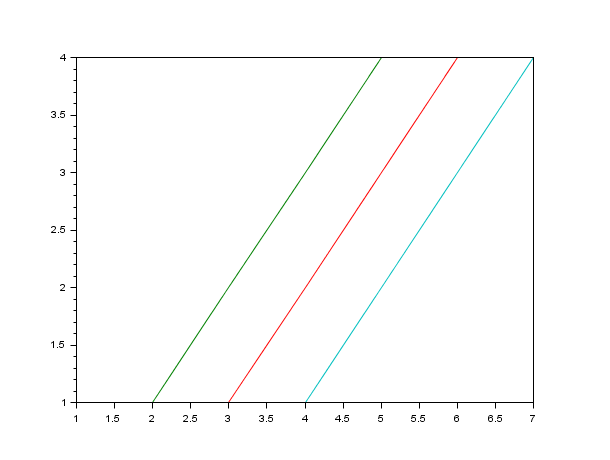
t=[1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 7]; clf(); cols = 1:4; // cols is transposed : notice the priority given to the columns treatment plot(t', cols) // equivalent to plot(t',[1 1 1 1;2 2 2 2;3 3 3 3;4 4 4 4]) plot(t', cols') // the same plot
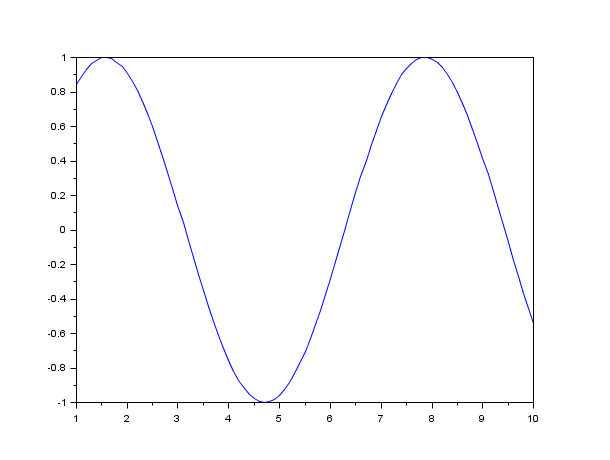
clf(); // y is a function defined by.. // ..a primitive plot(1:0.1:10,sin) // equivalent to plot(1:0.1:10,sin(1:0.1:10))
See also
- plot2d — 2D plot
- surf — 3D surface plot
- scf — set the current graphic figure (window)
- clf — Clears and resets a figure or a frame uicontrol
- xdel — delete a graphics window
- delete — delete a graphic entity and its children.
- LineSpec — to quickly customize the lines appearance in a plot
- GlobalProperty — to customize the objects appearance (curves, surfaces...) in a plot or surf command
| Report an issue | ||
| << paramfplot2d | 2d_plot | plot2d >> |