- Справка Scilab
- Signal Processing
- Filters
- How to design an elliptic filter
- analpf
- buttmag
- casc
- cheb1mag
- cheb2mag
- ell1mag
- eqfir
- eqiir
- faurre
- ffilt
- filt_sinc
- filter
- find_freq
- frmag
- fsfirlin
- group
- hilbert
- iir
- iirgroup
- iirlp
- kalm
- lev
- levin
- lindquist
- remez
- remezb
- sgolay
- sgolaydiff
- sgolayfilt
- srfaur
- srkf
- sskf
- syredi
- system
- trans
- wfir
- wfir_gui
- wiener
- wigner
- window
- yulewalk
- zpbutt
- zpch1
- zpch2
- zpell
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
levin
Toeplitz system solver by Levinson algorithm (multidimensional)
Syntax
[la,sig]=levin(n,cov)
Arguments
- n
A scalar with integer value: the maximum order of the filter
- cov
A
(nlag*d) x dmatrix. It contains theRk(d x dmatrices for ad-dimensional process) stored in the following way :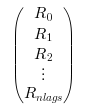
- la
A list, the successively calculated Levinson polynomials (degree 1 to
n), with coefficientsAk- sig
A list, the successive mean-square errors.
Description
function which solves recursively on n the following Toeplitz system (normal equations)
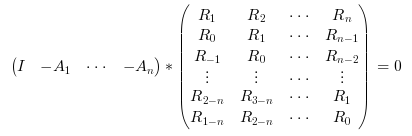
where {Rk;k=1:nlag} is the sequence of
nlag empirical covariances
Examples
//We use the 'levin' macro for solving the normal equations //on two examples: a one-dimensional and a two-dimensional process. //We need the covariance sequence of the stochastic process. //This example may usefully be compared with the results from //the 'phc' macro (see the corresponding help and example in it) // // //1) A one-dimensional process // ------------------------- // //We generate the process defined by two sinusoids (1Hz and 2 Hz) //in additive Gaussian noise (this is the observed process); //the simulated process is sampled at 10 Hz (step 0.1 in t, underafter). t1=0:.1:100;rand('normal'); y1=sin(2*%pi*t1)+sin(2*%pi*2*t1);y1=y1+rand(y1);plot(t1,y1); //covariance of y1 nlag=128; c1=corr(y1,nlag); c1=c1';//c1 needs to be given columnwise (see the section PARAMETERS of this help) //compute the filter for a maximum order of n=10 //la is a list-type variable each element of which //containing the filters of order ranging from 1 to n; (try varying n) //in the d-dimensional case this is a matrix polynomial (square, d X d) //sig gives, the same way, the mean-square error n=15; [la1,sig1]=levin(n,c1); //verify that the roots of 'la' contain the //frequency spectrum of the observed process y //(remember that y is sampled -in our example //at 10Hz (T=0.1s) so that we need to retrieve //the original frequencies (1Hz and 2 Hz) through //the log and correct scaling by the frequency sampling) //we verify this for each filter order for i=1:n, s1=roots(la1(i));s1=log(s1)/2/%pi/.1; //now we get the estimated poles (sorted, positive ones only !) s1=gsort(imag(s1));s1=s1(1:i/2);end; //the last two frequencies are the ones really present in the observed //process ---> the others are "artifacts" coming from the used model size. //This is related to the rather difficult problem of order estimation. // //2) A 2-dimensional process // ----------------------- //(4 frequencies 1, 2, 3, and 4 Hz, sampled at 0.1 Hz : // |y_1| y_1=sin(2*Pi*t)+sin(2*Pi*2*t)+Gaussian noise // y=| | with : // |y_2| y_2=sin(2*Pi*3*t)+sin(2*Pi*4*t)+Gaussian noise d=2;dt=0.1; nlag=64; t2=0:2*%pi*dt:100; y2=[sin(t2)+sin(2*t2)+rand(t2);sin(3*t2)+sin(4*t2)+rand(t2)]; c2=[]; for j=1:2, for k=1:2, c2=[c2;corr(y2(k,:),y2(j,:),nlag)];end;end; c2=matrix(c2,2,128);cov=[]; for j=1:64,cov=[cov;c2(:,(j-1)*d+1:j*d)];end;//covar. columnwise c2=cov; //in the multidimensional case, we have to compute the //roots of the determinant of the matrix polynomial //(easy in the 2-dimensional case but tricky if d>=3 !). //We just do that here for the maximum desired //filter order (n); mp is the matrix polynomial of degree n [la2,sig2]=levin(n,c2); mp=la2(n);determinant=mp(1,1)*mp(2,2)-mp(1,2)*mp(2,1); s2=roots(determinant);s2=log(s2)/2/%pi/0.1;//same trick as above for 1D process s2=gsort(imag(s2));s2=s2(1:d*n/2);//just the positive ones ! //There the order estimation problem is seen to be much more difficult ! //many artifacts ! The 4 frequencies are in the estimated spectrum //but beneath many non relevant others.
See also
- phc — Markovian representation
| Report an issue | ||
| << lev | Filters | lindquist >> |