- Scilab Help
- Control Systems - CACSD
- Linear System Representation
- abcd
- arma
- arma2p
- arma2ss
- armac
- bloc2ss
- cont_frm
- des2ss
- des2tf
- frep2tf
- lsslist
- markp2ss
- pfss
- pol2des
- sm2des
- sm2ss
- ss2des
- ss2ss
- ss2tf
- ss2zp
- ssprint
- ssrand
- sysconv
- sysdiag
- syslin
- syssize
- systmat
- tf2des
- tf2ss
- tf2zp
- trfmod
- zp2ss
- zp2tf
- zpk
- zpk2ss
- zpk2tf
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
syslin
linear system definition
Syntax
sl = syslin(dom, A, B, C) sl = syslin(dom, A, B, C, D) sl = syslin(dom, A, B, C, D, x0) sl = syslin(dom, N, D) sl = syslin(dom, H)
Arguments
- dom
character string (
'c','d'), or[]or a scalar.- A,B,C,D
matrices of the state-space representation (
Doptional with default value zero matrix). For improper systemsDis a polynomial matrix.- x0
vector (initial state; default value is
0)- N, D
polynomial matrices
- H
rational matrix or linear state space representation
- sl
tlist ("
syslin" list) representing the linear system
Description
syslin defines a linear system as a list and
checks consistency of data.
dom specifies the time domain of the system and
can have the following values:
dom='c' for a continuous time system,
dom='d' for a discrete time system,
n for a sampled system with sampling period
n (in seconds).
dom=[] if the time domain is undefined
State-space representation:
sl=syslin(dom,A,B,C [,D [,x0] ])
represents the system :
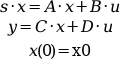
The output of syslin is a list of the following
form:
sl=tlist(['lss','A','B','C','D','X0','dt'],A,B,C,D,x0,dom)
Note that D is allowed to be a polynomial matrix
(improper systems).
Transfer matrix representation:
sl=syslin(dom,N,D) sl=syslin(dom,H)
The output of syslin is a list of the following
form : sl = rlist(N,D,dom) or
sl=rlist(H(2),H(3),dom).
Linear systems defined as syslin can be
manipulated as usual matrices (concatenation, extraction, transpose,
multiplication, etc) both in state-space or transfer
representation.
Most of state-space control functions receive a
syslin list as input instead of the four matrices
defining the system.
Examples
A=[0,1;0,0];B=[1;1];C=[1,1]; S1=syslin('c',A,B,C) //Linear system definition S1("A") //Display of A-matrix S1("X0"), S1("dt") // Display of X0 and time domain s=poly(0,'s'); D=s; S2=syslin('c',A,B,C,D) H1=(1+2*s)/s^2, S1bis=syslin('c',H1) H2=(1+2*s+s^3)/s^2, S2bis=syslin('c',H2) S1+S2 [S1,S2] ss2tf(S1)-S1bis S1bis+S2bis S1*S2bis size(S1)
See also
- tlist — Scilab object and typed list definition.
- lsslist — Scilab linear state space function definition
- rlist — Scilab rational fraction function definition
- ssrand — random system generator
- ss2tf — conversion from state-space to transfer function
- tf2ss — transfer to state-space
- dscr — discretization of linear system
- abcd — state-space matrices
| Report an issue | ||
| << sysdiag | Linear System Representation | syssize >> |