Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
However, this page did not exist in the previous stable version.
sysdiag
Create a block diagonal matrix from provided inputs or block diagonal system connection
Syntax
r=sysdiag(a1,a2,...,an)
Description
Returns the block-diagonal system made with subsystems put in the main diagonal
- ai
subsystems (i.e. gains, or linear systems in state-space or transfer form)
constant, boolean, polynomial or rational matrices of any size
- r
a matrix with a1, a2, a3, ... on the diagonal
Description
Given the inputs A, B and C,
the output will have these matrices arranged on the diagonal:
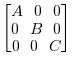 .
.
 | If all the input matrices are square, the output is known as a block diagonal matrix. |
 | Used in particular for system interconnections. |
Beside this function, you can also use sparse() primitive to build a block diagonal sparse matrix.
For boolean matrices sysdiag() always returns a zero one matrix in the corresponding block
("true" values are replaced by 1 and "false" value by 0).
sysdiag() cannot be used to arrange matrices made of character strings,
but you can overload it (see: overloading).
Remark
At most 17 arguments.
Examples
s=poly(0,'s') sysdiag(rand(2,2),1/(s+1),[1/(s-1);1/((s-2)*(s-3))]) sysdiag(tf2ss(1/s),1/(s+1),[1/(s-1);1/((s-2)*(s-3))])
// a matrix of doubles: A=[1 0; 0 1], B=[3 4 5; 6 7 8], C=7 D=sysdiag(A,B,C) // sysdiag([%t %f; %f %t], eye(2,2), ones(3,3)) // a polynomial matrix: s=%s; sysdiag([s 4*s; 4 s^4], [1 s^2 s+2; 3*s 2 s^2-1]) // a rational matrix: sysdiag([1/s 2*s/(4*s+3)], [s; 4; 1/(s^2+2*s+1)]) // a block diagonal sparse matrix: S=sysdiag([1 2; 3 4], [5 6; 7 8], [9 10; 11 12], [13 14; 15 16]) S=sparse(S)
See also
- brackets — Concatenation. Recipients of an assignment. Results of a function
- insertion — partial variable assignation or modification
- feedback — feedback operation
- diag — diagonal including or extracting
- bdiag — block diagonalization, generalized eigenvectors
- sparse — sparse matrix definition
- repmat — Replicate and tile an array
| Report an issue | ||
| << sysconv | Signal processing | trfmod >> |