- Scilabヘルプ
- Elementary Functions
- Trigonometry
- acos
- acosd
- acosh
- acoshm
- acosm
- acot
- acotd
- acoth
- acsc
- acscd
- acsch
- asec
- asecd
- asech
- asin
- asind
- asinh
- asinhm
- asinm
- atan
- atand
- atanh
- atanhm
- atanm
- cos
- cosd
- cosh
- coshm
- cosm
- cotd
- cotg
- coth
- cothm
- csc
- cscd
- csch
- csgn
- sec
- secd
- sech
- sin
- sinc
- sind
- sinh
- sinhm
- sinm
- tan
- tand
- tanh
- tanhm
- tanm
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
atan
2象限および 4象限逆正接
呼び出し手順
phi = atan(x) phi = atan(y, x)
引数
- x
実数または複素数のスカラー/ベクトル/行列
- phi
実数または複素数のスカラー/ベクトル/行列
- x, y
同じサイズの実数(スカラー,ベクトルまたは行列)
- phi
実数(スカラー,ベクトルまたは行列)
説明
最初の形式は2象限逆正接を計算します.
これは,tan(phi)の逆関数です.
xが実数の場合,
phiは 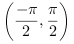 の範囲となります.
の範囲となります.
xが複素数の場合,
atanは二つの特異な分岐点
+%i, -%iを有し,
選択した分枝切断(branch cuts)は, 虚数の2つの半直線
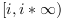 および
および
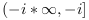 となります.
となります.
2番目の形式は4象限逆正接を計算します(Fortranの
atan2).
この場合,この関数は,複素数 x+i*y の偏角(角度)を
返します.
atan(y, x)の範囲は, 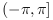 です.
です.
引数が実数の場合,x>0には
両形式とも同じ値となります.
引数がベクトルまたは行列の場合,
要素毎に評価が行われ,phiは
同じ大きさのベクトルまたは行列となります.
この際, phi(i, j) = atan(x(i, j)) または
phi(i,j) = atan(y(i, j), x(i, j))
となります.
例
| Report an issue | ||
| << asinm | Trigonometry | atand >> |