- Aide de Scilab
- Fonctions Elémentaires
- Trigonométrie
- acos
- acosd
- acosh
- acoshm
- acosm
- acot
- acotd
- acoth
- acsc
- acscd
- acsch
- asec
- asecd
- asech
- asin
- asind
- asinh
- asinhm
- asinm
- atan
- atand
- atanh
- atanhm
- atanm
- cos
- cosd
- cosh
- coshm
- cosm
- cotd
- cotg
- coth
- cothm
- csc
- cscd
- csch
- csgn
- sec
- secd
- sech
- sin
- sinc
- sind
- sinh
- sinhm
- sinm
- tan
- tand
- tanh
- tanhm
- tanm
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
acosh
cosinus hyperbolique inverse
Syntaxe
t = acosh(x)
Arguments
- x, t
Eléments ou tableaux de nombres réels ou complexes.
ta la taille dex.
Description
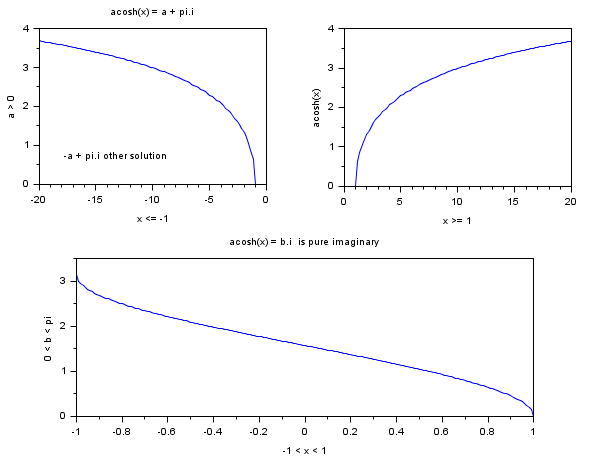
acosh(x) produit le résultat t
tel que
cosh(t)==x et par convention real(t)>=0.
cosh() étant une fonction symétrique, la ou les
valeurs -t sont toujours d'autres valeurs possibles.
Pour des valeurs d'entrée réelles -1 < x < 1,
real(t)==0 et imag(t)
est sur l'intervalle ]0, %pi[.
Pour des valeurs d'entrée x complexes,
imag(t) est sur l'intervalle [-pi, pi]
et toute valeur t + k*%pi*%i avec k entier relatif
est une autre réponse possible.
Graphes
Exemples
| Report an issue | ||
| << acosd | Trigonométrie | acoshm >> |