- Aide de Scilab
- Traitement du Signal
- Filtres
- analpf
- buttmag
- casc
- cheb1mag
- cheb2mag
- convol
- ell1mag
- eqfir
- eqiir
- faurre
- ffilt
- filt_sinc
- filter
- find_freq
- frmag
- fsfirlin
- group
- hilbert
- iir
- iirgroup
- iirlp
- kalm
- lev
- levin
- lindquist
- remez
- remezb
- srfaur
- srkf
- sskf
- syredi
- system
- trans
- wfir
- wfir_gui
- wiener
- wigner
- window
- yulewalk
- zpbutt
- zpch1
- zpch2
- zpell
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
filter
filters a data sequence using a digital filter
Syntax
[y,zf] = filter(B, A, x [,zi])
Arguments
- B
real vector : the coefficients of the filter numerator in decreasing power order, or a polynomial.
- A
real vector : the coefficients of the filter denominator in decreasing power order, or a polynomial.
- x
real row vector : the input signal
- zi
real row vector of length
max(length(a),length(b))-1: the initial condition relative to a "direct form II transposed" state space representation. The default value is a vector filled with zeros.- y
real row vector : the filtered signal.
- zf
real row vector : the final state. It can be used to filter a next batch of the input signal.
Description
This function filters a data sequence using a digital filter using a "direct form II transposed" implementation.
The filter canonical form is :
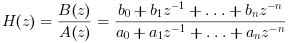
The algorithm uses the highest degree between degree(a) and degree(b) as value for n.
If the polynomial form is used for B (resp. for A) then a polynomial or a scalar must be used for A (resp. B).
References
Oppenheim, A. V. and R.W. Schafer. Discrete-Time Signal Processing, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989, pp. 311-312.
Examples
See also
| Report an issue | ||
| << filt_sinc | Filtres | find_freq >> |