Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
surf
3D surface plot
Calling Sequence
surf(Z,<GlobalProperty>) surf(Z,color,<GlobalProperty>) surf(X,Y,Z,<color>,<GlobalProperty>) surf(<axes_handle>,...)
Arguments
- Z
a real matrix defining the surface height. It can not be omitted. The Z data is a
mxnmatrix.- X,Y
two real matrices or vectors: always set together, these data defines a new standard grid. This new
XandYcomponents of the grid must matchZdimensions (see description below).- color
an optional real matrix defining a color value for each
(X(j),Y(i))point of the grid (see description below).- <GlobalProperty>
This optional argument represents a sequence of couple statements
{PropertyName,PropertyValue}that defines global objects' properties applied to all the curves created by this plot. For a complete view of the available properties (see GlobalProperty).- <axes_handle>
This optional argument forces the plot to appear inside the selected axes given by
axes_handlerather than the current axes (see gca).
Description
surf draws a colored parametric surface using a
rectangular grid defined by X and Y coordinates
(if {X,Y} are not specified, this grid is determined using
the dimensions of the Z matrix) ; at each point of this grid,
a Z coordinate is given using the Z matrix (only obligatory
data). surf has been created to better handle Matlab syntax.
To improve graphical compatibility, Matlab users should use
surf (rather than plot3d).
Data entry specification :
In this paragraph and to be more clear, we won't mention
GlobalProperty optional arguments as they do not interfer
with entry data (except for "Xdata", "Ydata" and
"Zdata" property, see GlobalProperty). It is
assumed that all those optional arguments could be present too.
If Z is the only matrix specified, surf(Z) plots the
matrix Z versus the grid defined by 1:size(Z,2)
along the x axis and 1:size(Z,1) along the y axis.
If a {X,Y,Z} triplet is given, Z must be a
matrix with size(Z)= [mxn],
X or Y can be :
a) a vector : if
Xis a vector, length(X)=n. Respectively, ifYis a vector, length(Y)=m.b) a matrix : in this case, size(
X) (or size(Y)) must equal size(Z).
Color entry specification :
As stated before, the surface is created over a rectangular grid
support. Let consider two independant variables i and
j such as :
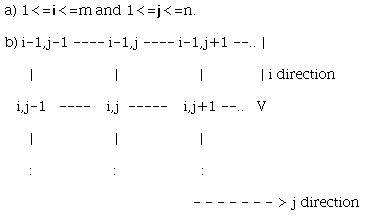
This imaginary rectangular grid is used to build the real surface
support onto the XY plane. Indeed,
X,Y and Z data have the same size
(even if X or Y is vector, see below) and can be
considered as 3 functions x(i,j), y(i,j) and
z(i,j) specifying the desired surface. If X or
Y are vectors, they are internally treated to produce good
matrices matching the Z matrix dimension (and the grid is
forcibly a rectangular region).
Considering the 3 functions x(i,j), y(i,j)
and z(i,j), the portion of surface defining between two
consecutive i and j is called a patch.
By default, when no color matrix is added to a surf call, the color
parameter is linked to the Z data. When a color
matrix is given, it can be applied to the patch in two different ways : at
the vertices or at the center of each patch.
That is why, if Z is a [mxn]
matrix, the C color matrix dimension can be
[mxn] (one color defined per vertex) or
[m-1xn-1] (one color per patch).
Color representation also varies when specifying some GlobalPropery:
The FaceColor property sets the shading mode : it can
be'interp' or 'flat' (default mode). When
'interp' is selected, we perform a bilinear color
interpolation onto the patch. If size(C) equals
size(Z)-1 (i.e. we provided only one color per patch) then
the color of the vertices defining the patch is set to the given color of
the patch.
When 'flat' (default mode) is enabled we use a color
faceted representation (one color per patch). If size(C)
equals size(Z) (i.e. we provided only one color per
vertices), the last row and column of C are ignored.
The GlobalProperty arguments sould be used to customize
the surface. Here is a brief description on how it works:
- GlobalProperty
This option may be used to specify how all the surfaces are drawn. It must always be a couple statement constituted of a string defining the
PropertyName, and its associated valuePropertyValue(which can be a string or an integer or... as well depending on the type of thePropertyName). Note that you can set multiple properties : the face & edge color, color data, color data mapping, marker color (foreground and background), the visibility, clipping and thickness of the edges of the surface... (see GlobalProperty )Note that all these properties can be (re-)set throught the surface entity properties (see surface_properties).
Remarks
By default, successive surface plots are superposed. To clear the
previous plot, use clf(). To enable auto_clear
mode as the default mode, edit your default axes doing:
da=gda();
da.auto_clear = 'on'
Enter the command surf to see a demo.
Examples
// Z initialisation Z= [ 0.0001 0.0013 0.0053 -0.0299 -0.1809 -0.2465 -0.1100 -0.0168 -0.0008 -0.0000 0.0005 0.0089 0.0259 -0.3673 -1.8670 -2.4736 -1.0866 -0.1602 -0.0067 0.0000 0.0004 0.0214 0.1739 -0.3147 -4.0919 -6.4101 -2.7589 -0.2779 0.0131 0.0020 -0.0088 -0.0871 0.0364 1.8559 1.4995 -2.2171 -0.2729 0.8368 0.2016 0.0130 -0.0308 -0.4313 -1.7334 -0.1148 3.0731 0.4444 2.6145 2.4410 0.4877 0.0301 -0.0336 -0.4990 -2.3552 -2.1722 0.8856 -0.0531 2.6416 2.4064 0.4771 0.0294 -0.0137 -0.1967 -0.8083 0.2289 3.3983 3.1955 2.4338 1.2129 0.2108 0.0125 -0.0014 -0.0017 0.3189 2.7414 7.1622 7.1361 3.1242 0.6633 0.0674 0.0030 0.0002 0.0104 0.1733 1.0852 2.6741 2.6725 1.1119 0.1973 0.0152 0.0005 0.0000 0.0012 0.0183 0.1099 0.2684 0.2683 0.1107 0.0190 0.0014 0.0000]; //simple surface surf(Z); // Note that X and Y are determined by Z dimensions //same surface with red face color and blue edges scf(2); // new figure number 2 surf(Z,'facecol','red','edgecol','blu") // X and Y initialisation // NB: here, X has the same lines and Y the same columns X = [ -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000]; Y= [ -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -3.0000 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.6667 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -1.0000 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 -0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 1.6667 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 2.3333 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000 3.0000]; // example 1 scf(3) surf(X,Y,Z) //example 2 // As you can see, the grid is not necessary rectangular scf(4) X(1,4) = -1.5; Y(1,4) = -3.5; Z(1,4) = -2; surf(X,Y,Z) // example 3 // X and Y are vectors => same behavior as sample 1 // With vectors, the grid is inevitably rectangular scf(5)// new figure number 5 X=[ -3.0000 -2.3333 -1.6667 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 1.0000 1.6667 2.3333 3.0000]; Y=X; surf(X,Y,Z) //LineSpec and GlobalProperty examples: xdel(winsid()) // destroy all existing figures surf(Z,Z+5) // color array specified e=gce(); e.cdata_mapping='direct' // default is 'scaled' relative to the colormap e.color_flag=3; // interpolated shading mode. The default is 4 ('flat' mode) for surf scf(2) surf(X,Y,Z,'colorda',ones(10,10),'edgeco','cya','marker','penta','markersiz',20,'markeredg','yel','ydata',56:65) scf(3) surf(Z,'cdatamapping','direct') scf(4) surf(Z,'facecol','interp') // interpolated shading mode (color_flag == 3) scf(10) axfig10=gca(); scf(11); surf(axfig10,Z,'ydat',[100:109],'marker','d','markerfac','green','markeredg','yel') // draw onto the axe of figure 10 xdel(winsid())
See Also
- plot2d — 2D plot
- clf — clear or reset the current graphic figure (window) to default values
- xdel — supprime des fenêtres graphiques
- delete — delete a graphic entity and its children.
- LineSpec — to quickly customize the lines appearance in a plot
- GlobalProperty — to customize the objects appearance (curves, surfaces...) in a plot or surf command.
Authors
F.Leray
| << plot3d3 | 3d_plot | surface_properties >> |