prod
product of array elements
Syntax
y=prod(x) y=prod(x,orientation) y=prod(x,outtype) y=prod(x,orientation,outtype)
Arguments
- x
an array of reals, complex, booleans, polynomials or rational fractions.
- orientation
it can be either
a string with possible values
"*","r","c"or"m"a number with positive integer value
- outtype
a string with possible values
"native"or"double".- y
scalar or array
Description
For an array x,
y=prod(x) returns in the scalar y the
product of all the elements of x.
y=prod(x,orientation) returns in
y the product of x along the
dimension given by orientation:
if
orientationis equal to 1 or "r" then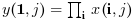
or
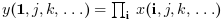
if
orientationis equal to 2 or "c" then: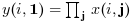
or
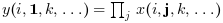
if
orientationis equal to n then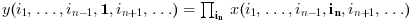
y=prod(x,"*")is equivalent toy=prod(x)y=prod(x,"m")is equivalent toy=prod(x,orientation)whereorientationis the index of the first dimension ofxthat is greater than 1.
The outtype argument rules the way the product is done:
For arrays of floats, of polynomials, of rational fractions, the evaluation is always done using floating points computations. The
"double"or"native"options are equivalent.For arrays of integers,
if
outtype="native"the evaluation is done using integer computations (modulo 2^b, where b is the number of bits used),if
outtype="double"the evaluation is done using floating point computations.The default value is
outtype="native".For arrays of booleans,
if
outtype="native"the evaluation is done using boolean computations (* is replaced by &),if
outtype="double"the evaluation is done using floating point computations (%t values are replaced by 1 and %f values by 0).The default value is
outtype="double". This option is used for Matlab compatibility.
 | This function applies with identical rules to sparse matrices. |
Examples
| Report an issue | ||
| << or | Matrix operations | sign >> |