derivat
derivative of polynomials or of rationals
Syntax
pd = derivat(p)
Arguments
- p, pd
arrays of polynomials or of rationals
Description
The derivat() function works with expressions like
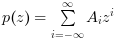 which consists of functions of linear combinations with integer exponents of one variable (in the example denoted by z).
which consists of functions of linear combinations with integer exponents of one variable (in the example denoted by z).
The function derivat() implements the analytical derivation of p(z), giving the following result.
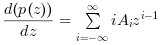
Examples
s = poly(0,'s'); derivat(1/s) // -1/s^2;
p1 = poly([1 -2 1], 'x', 'coeff') derivat(p1)
p2 = poly([1 -4 2], 'y', 'coeff') derivat(p2)
p4 = poly([-1 1], 't', 'roots') derivat(p4)
s = %s; p5 = s^(-1) + 2 + 3*s derivat(p5)
See also
- polyint — Polynomial integration
| Report an issue | ||
| << degree | Polynomials | determ >> |