noisegen
noise generation (obsolete)
Syntax
b = noisegen(pas, Tmax, sig)
Arguments
- pas
real scalar, the time increment
- Tmax
real scalar, the final time of the interval of noise generation
- sig
real scalar, the standard deviation of the noise
Description
 | noisegen() is obsolete. It will be removed from Scilab 6.1.x.
Please use grand() instead. Examples (clearer, shorter, and more powerful) follow:
100 10-point wide steps with random amplitudes of normal distribution of mean 1 and standard deviation 0.7: 40 15-point wide steps with random amplitudes of uniform distribution in [1 3], with initial level 0.5 and final level hold: |
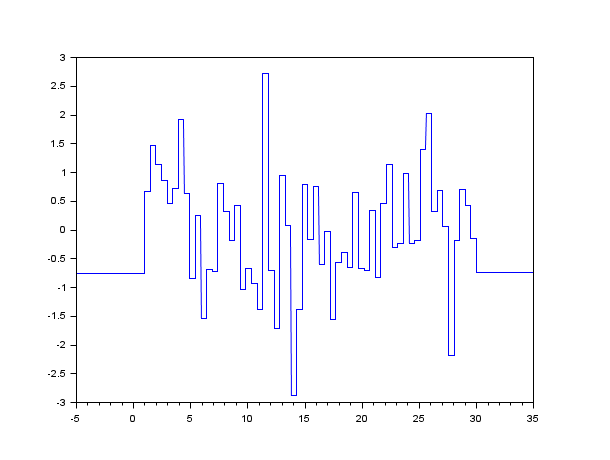
noisegen() generates a Scilab function b = Noise(t)
where Noise(t) is a piecewise constant function
(constant on [k*pas, (k+1)*pas]). The value on each constant
interval are random values from i.i.d Gaussian variables of
standard deviation sig. The function is constant for t <= 0 and
t >= Tmax.
 |
Examples
Example #1: noisegen()
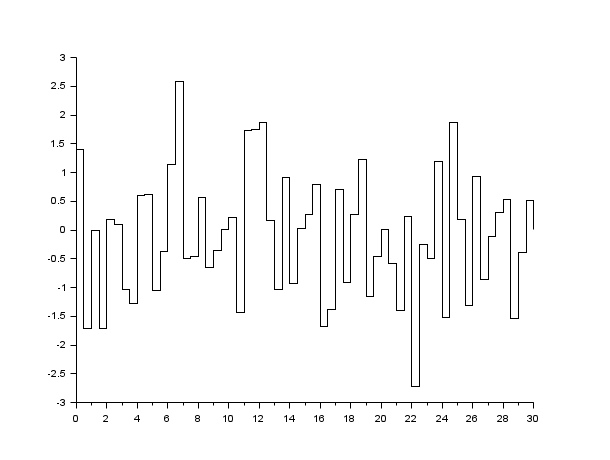
Example #2: rand()
// Plot a zero mean gaussian white noise with the variance 1. // To use a different variance, multiply rand() by the square root of the variance. t = 0:.5:30; sig = 1; // Standard deviation of the white gaussian noise noise = sig*rand(t, "normal"); plot2d2(t, noise);
History
| Versão | Descrição |
| 6.1.0 | noisegen() is obsolete. It will be removed from Scilab 6.1.x. Please replace it with grand() and .*. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << grand | random | prbs_a >> |