Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
corr
correlation, covariance
Syntax
[cov,Mean] = corr(x,[y],nlags) [cov,Mean] = corr('fft',xmacro,[ymacro],n,sect) [w,xu] = corr('updt',x1,[y1],w0) [w,xu] = corr('updt',x2,[y2],w,xu) ... wk = corr('updt',xk,[yk],w,xu)
Arguments
- x
a real vector
- y
a real vector, default value x.
- nlags
integer, number of correlation coefficients desired.
- xmacro
a scilab external (see below).
- ymacro
a scilab external (see below), default value xmacro
- n
an integer, total size of the sequence (see below).
- sect
size of sections of the sequence (see below).
- xi
a real vector
- yi
a real vector,default value xi.
- cov
real vector, the correlation coefficients
- Mean
real number or vector, the mean of x and if given y
Description
corr(x,y,…) computes
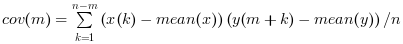 for
for m = 0, …, nlag-1.
Note that if x and y sequences are differents corr(x,y,...) is different with corr(y,x,...)
- Short sequences
[cov,Mean]=corr(x,[y],nlags)returns the first nlags correlation coefficients and Mean =mean(x)(mean of[x,y]ifyis an argument). The sequencex(resp.y) is assumed real, andxandyare of same dimension n.- Long sequences
[cov,Mean]=corr('fft',xmacro,[ymacro],n,sect). Herexmacrois eithera function of type
[xx]=xmacro(sect,istart)which returns a vectorxxof dimensionnsectcontaining the part of the sequence with indices fromistarttoistart+sect-1.a fortran subroutine or C procedure which performs the same calculation. (See the source code of
dgetxfor an example).
n= total size of the sequence.sect= size of sections of the sequence.sectmust be a power of 2.covhas dimensionsect. Calculation is performed by FFT.- Updating method
[w,xu]=corr('updt',x1,[y1],w0) [w,xu]=corr('updt',x2,[y2],w,xu) ... wk=corr('updt',xk,[yk],w,xu)
With this syntax the calculation is updated at each call to
corr.w0 = 0*ones(1,2*nlags); nlags = power of 2.
x1,x2,...are parts ofxsuch thatx=[x1,x2,...]and sizes ofxia power of 2. To getnlagscoefficients a final fft must be performedc=fft(w,1)/n;cov=c(1nlags)(nis the size ofx (y)). Caution: this syntax assumes thatxmean = ymean = 0.
Examples
x=%pi/10:%pi/10:102.4*%pi; rand('seed');rand('normal'); y=[.8*sin(x)+.8*sin(2*x)+rand(x);.8*sin(x)+.8*sin(1.99*x)+rand(x)]; c=[]; for j=1:2,for k=1:2,c=[c;corr(y(k,:),y(j,:),64)];end;end; c=matrix(c,2,128);cov=[]; for j=1:64,cov=[cov;c(:,(j-1)*2+1:2*j)];end; rand('unif') rand('normal');x=rand(1,256);y=-x; deff('[z]=xx(inc,is)','z=x(is:is+inc-1)'); deff('[z]=yy(inc,is)','z=y(is:is+inc-1)'); [c,mxy]=corr(x,y,32); x=x-mxy(1)*ones(x);y=y-mxy(2)*ones(y); //centring c1=corr(x,y,32);c2=corr(x,32); norm(c1+c2,1) [c3,m3]=corr('fft',xx,yy,256,32); norm(c1-c3,1) [c4,m4]=corr('fft',xx,256,32); norm(m3,1),norm(m4,1) norm(c3-c1,1),norm(c4-c2,1) x1=x(1:128);x2=x(129:256); y1=y(1:128);y2=y(129:256); w0=0*ones(1:64); //32 coeffs [w1,xu]=corr('u',x1,y1,w0);w2=corr('u',x2,y2,w1,xu); zz=real(fft(w2,1))/256;c5=zz(1:32); norm(c5-c1,1) [w1,xu]=corr('u',x1,w0);w2=corr('u',x2,w1,xu); zz=real(fft(w2,1))/256;c6=zz(1:32); norm(c6-c2,1) rand('unif') // test for Fortran or C external // deff('[y]=xmacro(sec,ist)','y=sin(ist:(ist+sec-1))'); x=xmacro(100,1); [cc1,mm1]=corr(x,2^3); [cc,mm]=corr('fft',xmacro,100,2^3); [cc2,mm2]=corr('fft','corexx',100,2^3); [max(abs(cc-cc1)),max(abs(mm-mm1)),max(abs(cc-cc2)),max(abs(mm-mm2))] deff('[y]=ymacro(sec,ist)','y=cos(ist:(ist+sec-1))'); y=ymacro(100,1); [cc1,mm1]=corr(x,y,2^3); [cc,mm]=corr('fft',xmacro,ymacro,100,2^3); [cc2,mm2]=corr('fft','corexx','corexy',100,2^3); [max(abs(cc-cc1)),max(abs(mm-mm1)),max(abs(cc-cc2)),max(abs(mm-mm2))]
See also
| Report an issue | ||
| << convol2d | Convolution - Correlation | hank >> |