Scilab 6.0.2
- Aide de Scilab
- Traitement du Signal
- Filtrage
- How to design an elliptic filter
- analpf
- buttmag
- casc
- cheb1mag
- cheb2mag
- ell1mag
- eqfir
- eqiir
- faurre
- ffilt
- filt_sinc
- filter
- find_freq
- frmag
- fsfirlin
- group
- hilbert
- iir
- iirgroup
- iirlp
- kalm
- lev
- levin
- lindquist
- remez
- remezb
- srfaur
- srkf
- sskf
- syredi
- system
- trans
- wfir
- wfir_gui
- wiener
- wigner
- window
- yulewalk
- zpbutt
- zpch1
- zpch2
- zpell
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
fsfirlin
design of FIR, linear phase filters, frequency sampling technique
Syntax
[hst]=fsfirlin(hd,flag)
Arguments
- hd
vector of desired frequency response samples
- flag
is equal to 1 or 2, according to the choice of type 1 or type 2 design
- hst
vector giving the approximated continuous response on a dense grid of frequencies
Description
function for the design of FIR, linear phase filters using the frequency sampling technique
Examples
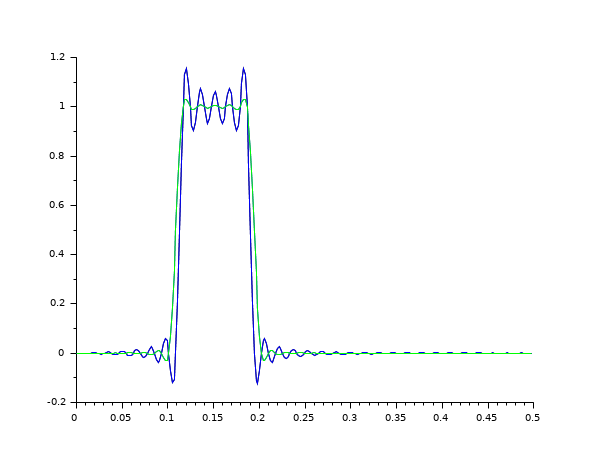
// //Example of how to use the fsfirlin macro for the design //of an FIR filter by a frequency sampling technique. // //Two filters are designed : the first (response hst1) with //abrupt transitions from 0 to 1 between passbands and stop //bands; the second (response hst2) with one sample in each //transition band (amplitude 0.5) for smoothing. // hd=[zeros(1,15) ones(1,10) zeros(1,39)];//desired samples hst1=fsfirlin(hd,1);//filter with no sample in the transition hd(15)=.5;hd(26)=.5;//samples in the transition bands hst2=fsfirlin(hd,1);//corresponding filter pas=1/prod(size(hst1))*.5; fg=0:pas:.5;//normalized frequencies grid plot2d([1 1].*.fg(1:257)',[hst1' hst2']); // 2nd example hd=[0*ones(1,15) ones(1,10) 0*ones(1,39)];//desired samples hst1=fsfirlin(hd,1);//filter with no sample in the transition hd(15)=.5;hd(26)=.5;//samples in the transition bands hst2=fsfirlin(hd,1);//corresponding filter pas=1/prod(size(hst1))*.5; fg=0:pas:.5;//normalized frequencies grid n=prod(size(hst1)) plot(fg(1:n),hst1); plot2d(fg(1:n)',hst2',[3],"000");
| Report an issue | ||
| << frmag | Filtrage | group >> |