Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
linear_interpn
n dimensional linear interpolation
Syntax
vp = linear_interpn(xp1,xp2,..,xpn, x1, ..., xn, v [,out_mode])
Arguments
- xp1, xp2, .., xpn
real vectors (or matrices) of same size
- x1 ,x2, ..., xn
strictly increasing row vectors (with at least 2 components) defining the n dimensional interpolation grid
- v
vector (case n=1), matrix (case n=2) or hypermatrix (case n > 2) with the values of the underlying interpolated function at the grid points.
- out_mode
(optional) string defining the evaluation outside the grid (extrapolation)
- vp
vector or matrix of same size than
xp1, ..., xpn
Description
Given a n dimensional grid defined by the n vectors x1 ,x2,
..., xn
and the values v of a function (says
f) at the grid points :
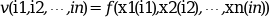
this function computes the linear interpolant of
f from the grid (called s in the
following) at the points which coordinates are defined by the vectors (or
matrices) xp1, xp2, ..., xpn:
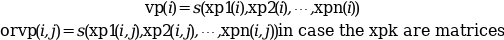
The out_mode parameter set the evaluation rule
for extrapolation: if we note
Pi=(xp1(i),xp2(i),...,xpn(i)) then
out_mode defines the evaluation rule when:
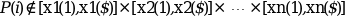
The different choices are:
- "by_zero"
an extrapolation by zero is done
- "by_nan"
extrapolation by Nan
- "C0"
the extrapolation is defined as follows:
- "natural"
the extrapolation is done by using the nearest n-linear patch from the point.
- "periodic"
sis extended by periodicity.
Examples
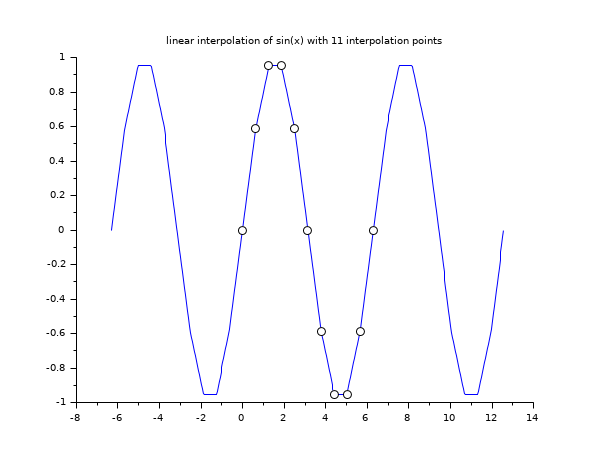
// example 1 : 1d linear interpolation x = linspace(0,2*%pi,11); y = sin(x); xx = linspace(-2*%pi,4*%pi,400)'; yy = linear_interpn(xx, x, y, "periodic"); clf() plot2d(xx,yy,style=2) plot2d(x,y,style=-9, strf="000") xtitle("linear interpolation of sin(x) with 11 interpolation points")
// example 2 : bilinear interpolation n = 8; x = linspace(0,2*%pi,n); y = x; z = 2*sin(x')*sin(y); xx = linspace(0,2*%pi, 40); [xp,yp] = ndgrid(xx,xx); zp = linear_interpn(xp,yp, x, y, z); clf() plot3d(xx, xx, zp, flag=[2 6 4]) [xg,yg] = ndgrid(x,x); param3d1(xg,yg, list(z,-9*ones(1,n)), flag=[0 0]) xtitle("Bilinear interpolation of 2sin(x)sin(y)") legends("interpolation points",-9,1) show_window()
// example 3 : bilinear interpolation and experimentation // with all the outmode features nx = 20; ny = 30; x = linspace(0,1,nx); y = linspace(0,2, ny); [X,Y] = ndgrid(x,y); z = 0.4*cos(2*%pi*X).*cos(%pi*Y); nxp = 60 ; nyp = 120; xp = linspace(-0.5,1.5, nxp); yp = linspace(-0.5,2.5, nyp); [XP,YP] = ndgrid(xp,yp); zp1 = linear_interpn(XP, YP, x, y, z, "natural"); zp2 = linear_interpn(XP, YP, x, y, z, "periodic"); zp3 = linear_interpn(XP, YP, x, y, z, "C0"); zp4 = linear_interpn(XP, YP, x, y, z, "by_zero"); zp5 = linear_interpn(XP, YP, x, y, z, "by_nan"); clf() subplot(2,3,1) plot3d(x, y, z, leg="x@y@z", flag = [2 4 4]) xtitle("initial function 0.4 cos(2 pi x) cos(pi y)") subplot(2,3,2) plot3d(xp, yp, zp1, leg="x@y@z", flag = [2 4 4]) xtitle("Natural") subplot(2,3,3) plot3d(xp, yp, zp2, leg="x@y@z", flag = [2 4 4]) xtitle("Periodic") subplot(2,3,4) plot3d(xp, yp, zp3, leg="x@y@z", flag = [2 4 4]) xtitle("C0") subplot(2,3,5) plot3d(xp, yp, zp4, leg="x@y@z", flag = [2 4 4]) xtitle("by_zero") subplot(2,3,6) plot3d(xp, yp, zp5, leg="x@y@z", flag = [2 4 4]) xtitle("by_nan") show_window()
// example 4 : trilinear interpolation (see splin3d help // page which have the same example with // tricubic spline interpolation) exec("SCI/modules/interpolation/demos/interp_demo.sci"); func = "v=(x-0.5).^2 + (y-0.5).^3 + (z-0.5).^2"; deff("v=f(x,y,z)",func); n = 5; x = linspace(0,1,n); y=x; z=x; [X,Y,Z] = ndgrid(x,y,z); V = f(X,Y,Z); // compute (and display) the linear interpolant on some slices m = 41; dir = ["z=" "z=" "z=" "x=" "y="]; val = [ 0.1 0.5 0.9 0.5 0.5]; ebox = [0 1 0 1 0 1]; XF=[]; YF=[]; ZF=[]; VF=[]; for i = 1:length(val) [Xm,Xp,Ym,Yp,Zm,Zp] = slice_parallelepiped(dir(i), val(i), ebox, m, m, m); Vm = linear_interpn(Xm,Ym,Zm, x, y, z, V); [xf,yf,zf,vf] = nf3dq(Xm,Ym,Zm,Vm,1); XF = [XF xf]; YF = [YF yf]; ZF = [ZF zf]; VF = [VF vf]; Vp = linear_interpn(Xp,Yp,Zp, x, y, z, V); [xf,yf,zf,vf] = nf3dq(Xp,Yp,Zp,Vp,1); XF = [XF xf]; YF = [YF yf]; ZF = [ZF zf]; VF = [VF vf]; end nb_col = 128; vmin = min(VF); vmax = max(VF); color = dsearch(VF,linspace(vmin,vmax,nb_col+1)); clf() gcf().color_map = jetcolormap(nb_col); gca().hiddencolor = gca().background; colorbar(vmin,vmax) plot3d(XF, YF, list(ZF,color), flag=[-1 6 4]) xtitle("tri-linear interpolation of "+func) show_window()
See also
History
| Version | Description |
| 5.4.0 | previously, imaginary part of input arguments were implicitly ignored. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << interpln | Interpolation | lsq_splin >> |