Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
datafit
Parameter identification based on measured data
Syntax
[p,err]=datafit([iprint,] G [,DG],Z [,W],[contr],p0,[algo],[df0,[mem]], [work],[stop],['in'])
Arguments
- iprint
scalar argument used to set the trace mode.
iprint=0nothing (except errors) is reported,iprint=1initial and final reports,iprint=2adds a report per iteration,iprint>2add reports on linear search. Warning: most of these reports are written on the Scilab standard output.
Warning: most of these reports are written on the Scilab standard output.- G
function descriptor (e=G(p,z), e: ne x 1, p: np x 1, z: nz x 1)
- DG
partial of G wrt p function descriptor (optional; S=DG(p,z), S: ne x np)
- Z
matrix [z_1,z_2,...z_n] where z_i (nz x 1) is the ith measurement
- W
weighting matrix of size ne x ne (optional; default no ponderation)
- contr
'b',binf,bsupwithbinfandbsupreal vectors with same dimension asp0.binfandbsupare lower and upper bounds onp.- p0
initial guess (size np x 1)
- algo
'qn'or'gc'or'nd'. This string stands for quasi-Newton (default), conjugate gradient or non-differentiable respectively. Note that'nd'does not accept bounds onx).- df0
real scalar. Guessed decreasing of
fat first iteration. (df0=1is the default value).- mem :
integer, number of variables used to approximate the Hessian, (
algo='gc' or 'nd'). Default value is around 6.- stop
sequence of optional parameters controlling the convergence of the algorithm.
stop= 'ar',nap, [iter [,epsg [,epsf [,epsx]]]]- "ar"
reserved keyword for stopping rule selection defined as follows:
- nap
maximum number of calls to
funallowed.- iter
maximum number of iterations allowed.
- epsg
threshold on gradient norm.
- epsf
threshold controlling decreasing of
f- epsx
threshold controlling variation of
x. This vector (possibly matrix) of same size asx0can be used to scalex.
- "in"
reserved keyword for initialization of parameters used when
funin given as a Fortran routine (see below).- p
Column vector, optimal solution found
- err
scalar, least square error.
Description
datafit is used for fitting data to a model. For
a given function G(p,z), this function finds the best
vector of parameters p for approximating
G(p,z_i)=0 for a set of measurement vectors
z_i. Vector p is found by minimizing
G(p,z_1)'WG(p,z_1)+G(p,z_2)'WG(p,z_2)+...+G(p,z_n)'WG(p,z_n)
Examples
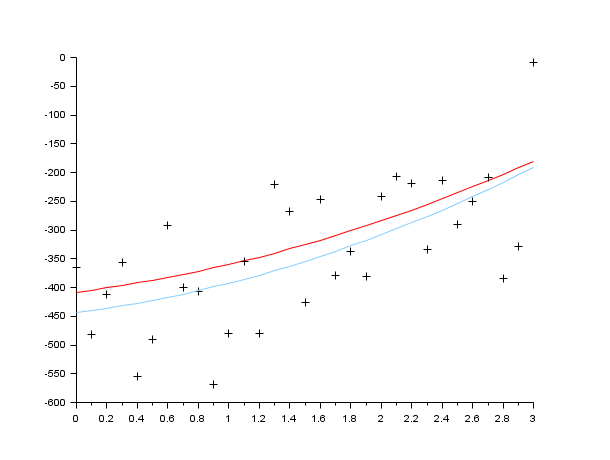
//generate the data function y=FF(x, p) y=p(1)*(x-p(2))+p(3)*x.*x endfunction X=[]; Y=[]; pg=[34;12;14] //parameter used to generate data for x=0:.1:3 Y=[Y,FF(x,pg)+100*(rand()-.5)]; X=[X,x]; end Z=[Y;X]; //The criterion function function e=G(p, z), y=z(1),x=z(2); e=y-FF(x,p), endfunction //Solve the problem p0=[3;5;10] [p,err]=datafit(G,Z,p0); scf(0);clf() plot2d(X,FF(X,pg),5) //the curve without noise plot2d(X,Y,-1) // the noisy data plot2d(X,FF(X,p),12) //the solution
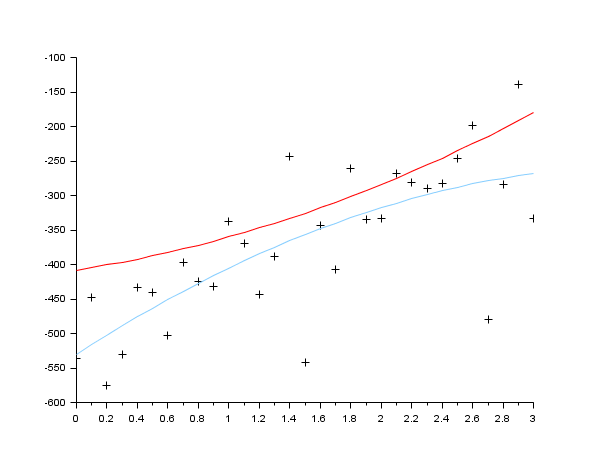
//generate the data function y=FF(x, p) y=p(1)*(x-p(2))+p(3)*x.*x endfunction //the gradient of the criterion function function s=DG(p, z), a=p(1),b=p(2),c=p(3),y=z(1),x=z(2), s=-[x-b,-a,x*x] endfunction function e=G(p, z), y=z(1),x=z(2); e=y-FF(x,p), endfunction X=[];Y=[]; pg=[34;12;14] for x=0:.1:3 Y=[Y,FF(x,pg)+100*(rand()-.5)]; X=[X,x]; end Z=[Y;X]; p0=[3;5;10] [p,err]=datafit(G,DG,Z,p0); scf(1); clf() plot2d(X,FF(X,pg),5) //the curve without noise plot2d(X,Y,-1) // the noisy data plot2d(X,FF(X,p),12) //the solution
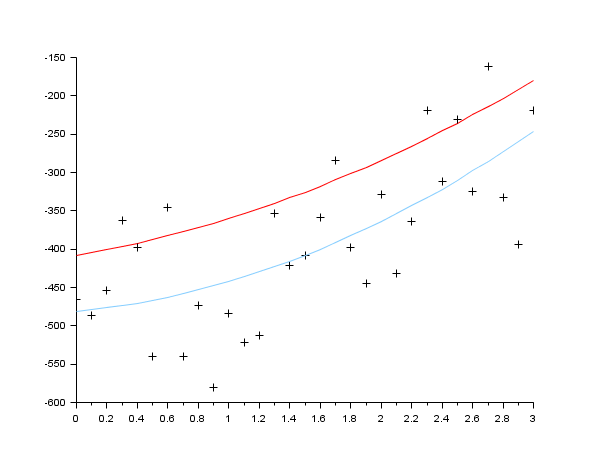
//generate the data function y=FF(x, p) y=p(1)*(x-p(2))+p(3)*x.*x endfunction //the gradient of the criterion function function s=DG(p, z), a=p(1),b=p(2),c=p(3),y=z(1),x=z(2), s=-[x-b,-a,x*x] endfunction function e=G(p, z), y=z(1),x=z(2); e=y-FF(x,p), endfunction X=[];Y=[]; pg=[34;12;14] for x=0:.1:3 Y=[Y,FF(x,pg)+100*(rand()-.5)]; X=[X,x]; end Z=[Y;X]; p0=[3;5;10] // Add some bounds on the estimate of the parameters // We want positive estimation (the result will not change) [p,err]=datafit(G,DG,Z,'b',[0;0;0],[%inf;%inf;%inf],p0,algo='gc'); scf(1); clf() plot2d(X,FF(X,pg),5) //the curve without noise plot2d(X,Y,-1) // the noisy data plot2d(X,FF(X,p),12) //the solution
See also
| Report an issue | ||
| << Nonlinear Least Squares | Nonlinear Least Squares | leastsq >> |