Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
qp_solve
組み込みの線形二次計画ソルバー
呼び出し手順
[x [,iact [,iter [,f]]]] = qp_solve(Q, p, C, b, me)
パラメータ
- Q
実数正定対称行列 (次元
n x n).- p
実数 (列) ベクトル (次元
n)- C
実数行列 (次元
(me + md) x n). この行列は通常行列または疎行列とすることができます.- b
RHS 列ベクトル (次元
m=(me + md))- me
等式拘束の数 (すなわち
x'*C(:,1:me) = b(1:me)')- x
見つかった最適解.
- iact
ベクトル, アクティブな拘束のインジケータ. 最初の 非ゼロのエントリは アクティブの拘束のインデックスを出力します
- iter
2x1ベクトル, 最初の要素には "main" 反復の数を出力します. 2番目の要素には,アクティブになった後に削除された拘束の数を出力します.
説明
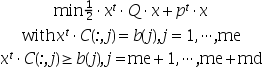
この関数は,Qが対称正定であることを必要とします.
この仮定が満たされない場合には, quaproツールボックスで
指定されたquapro 関数を使用することができます.
例
// 以下のような x ( R^6)を探す: // x'*C1 = b1 (3 個の等式拘束 すなわち me=3) C1= [ 1,-1, 2; -1, 0, 5; 1,-3, 3; 0,-4, 0; 3, 5, 1; 1, 6, 0]; b1=[1;2;3]; // x'*C2 >= b2 (2 個の不等式拘束) C2= [ 0 ,1; -1, 0; 0,-2; -1,-1; -2,-1; 1, 0]; b2=[ 1;-2.5]; // 以下の条件のもとで 0.5*x'*Q*x + p'*x を最小化 p=[-1;-2;-3;-4;-5;-6]; Q=eye(6,6); me=3; [x,iact,iter,f]=qp_solve(Q,p,[C1 C2],[b1;b2],me) // 線形拘束 (1 から 4) のみアクティブ
参照
- optim — non-linear optimization routine
- qld — linear quadratic programming solver
- qpsolve — 線形二次計画ソルバー
ツールボックス "quapro" も特にQが
特異な場合には有用かもしれません.
参考文献
Goldfarb, D. and Idnani, A. (1982). "Dual and Primal-Dual Methods for Solving Strictly Convex Quadratic Programs", in J.P. Hennart (ed.), Numerical Analysis, Proceedings, Cocoyoc, Mexico 1981, Vol. 909 of Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 226-239.
Goldfarb, D. and Idnani, A. (1983). "A numerically stable dual method for solving strictly convex quadratic programs", Mathematical Programming 27: 1-33.
QuadProg (Quadratic Programming Routines), Berwin A Turlach,http://www.maths.uwa.edu.au/~berwin/software/quadprog.html
使用される関数
Goldfarb/Idnani アルゴリズムに基づきBerwin A. Turlach により開発されたqpgen2.f and >qpgen1.f (または QP.solve.f)
| Report an issue | ||
| << fsolve | Optimization and Simulation | qpsolve >> |