Scilab 5.4.1
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
remezb
Minimax approximation of magnitude response
Calling Sequence
[an]=remezb(nc,fg,ds,wt)
Arguments
- nc
Number of cosine functions
- fg
Grid of frequency points in [0,.5)
- ds
Desired magnitude on grid
fg- wt
Weighting function on error on grid
fg- an
Cosine filter coefficients
Description
Minimax approximation of a frequency domain
magnitude response. The approximation takes
the form h = sum[a(n)*cos(wn)]
for n=0,1,...,nc. An FIR, linear-phase filter
can be obtained from the output of the function
by using the following commands
hn(1:nc-1)=an(nc:-1:2)/2; hn(nc)=an(1); hn(nc+1:2*nc-1)=an(2:nc)/2;
Examples
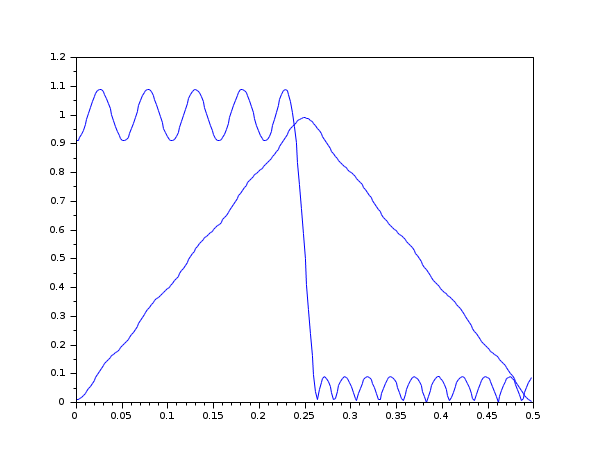
// Choose the number of cosine functions and create a dense grid // in [0,.24) and [.26,.5) nc=21;ngrid=nc*16; fg=.24*(0:ngrid/2-1)/(ngrid/2-1); fg(ngrid/2+1:ngrid)=fg(1:ngrid/2)+.26*ones(1:ngrid/2); // Specify a low pass filter magnitude for the desired response ds(1:ngrid/2)=ones(1:ngrid/2); ds(ngrid/2+1:ngrid)=zeros(1:ngrid/2); // Specify a uniform weighting function wt=ones(fg); // Run remezb an=remezb(nc,fg,ds,wt) // Make a linear phase FIR filter hn(1:nc-1)=an(nc:-1:2)/2; hn(nc)=an(1); hn(nc+1:2*nc-1)=an(2:nc)/2; // Plot the filter's magnitude response plot(.5*(0:255)/256,frmag(hn,256)); // Choose the number of cosine functions and create a dense grid in [0,.5) nc=21; ngrid=nc*16; fg=.5*(0:(ngrid-1))/ngrid; // Specify a triangular shaped magnitude for the desired response ds(1:ngrid/2)=(0:ngrid/2-1)/(ngrid/2-1); ds(ngrid/2+1:ngrid)=ds(ngrid/2:-1:1); // Specify a uniform weighting function wt=ones(fg); // Run remezb an=remezb(nc,fg,ds,wt) // Make a linear phase FIR filter hn(1:nc-1)=an(nc:-1:2)/2; hn(nc)=an(1); hn(nc+1:2*nc-1)=an(2:nc)/2; // Plot the filter's magnitude response plot(.5*(0:255)/256,frmag(hn,256));
See Also
- eqfir — minimax approximation of FIR filter
| Report an issue | ||
| << lindquist | filters | srfaur >> |