Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
SHIFT
Shift/Rotates Bits
Block Screenshot

Contents
Palette
Description
This block shifts the bits of the input signal. In this operation the digits are moved to the right or to the left.The user can choose the rule to shifts the bits that can be normal or cycle by setting the Shift Type parameter to 0 or 1. The number and the direction of the shifts are set with the Number of Bits to Shift Left. If this number is positive the input is shifted to the left, otherwise it is shifted to the right.
When the Shift Type parameter is :
0 : an arithmetic shift is applied to the input signal. In this case, the bits that are shifted out of either end are discarded. Zeros are shifted in on the right, in the case of left shift; in the case of right shifts, copies of the sign bit is shifted in on the left.
By example, the one bit shift right gives:
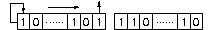 and the one bit shift left gives:
and the one bit shift left gives: 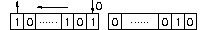
1 : a circular shift is applied to the input signal. In this case, the bits are rotated as if the left and right ends of the register are joined. The value that is shifted in on the right during a left-shift is whatever values was shifted out on the left, and vice versa.
By example, the one bit rotation right gives:
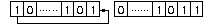 and the one bit rotation left gives:
and the one bit rotation left gives: 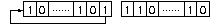 .
.
The shift register makes a multiplication by 2n
(arithmetic left shift) or an integer division by 2n
(arithmetic right shift), where n is the number of bit shifts.
It can also be used to serialize data or to create a memory buffer.
Data types
The block supports the following types :
Input : scalar. All Scilab's integer type (Data Type parameter).
Output : same type and dimensions than input.
Dialog box
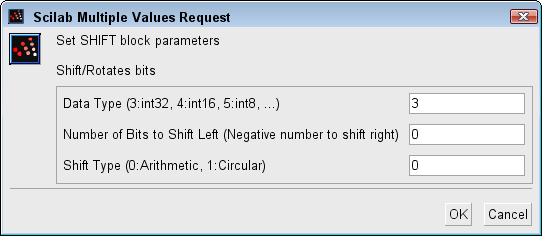
Data Type (3:int32, 4:int16, 5:int8, ...)
It indicates the type of the input/output : between 3 and 8.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1.
Number of Bits to Shift Left (Negative number to shift right)
It indicates the number of bits the input signal is shifted/rotated. A positive value indicates a shift left, a negative value a shift right. The index must be, when the type is :
int32 or uint32: positive and less than 32.
int16 or uint16: positive and less than 16.
int8 or uint8: positive and less than 8.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1.
Shift Type (0:Arithmetic, 1:Circular)
O or 1. It indicates the rule used to shift the bits. It can be arithmetic or circular. When it is :
0, an arithmetic shift is applied to the input signal.
1, a circular shift is applied to the input signal.
See description for more information.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1.
Default properties
always active: no
direct-feedthrough: yes
zero-crossing: no
mode: no
regular inputs:
- port 1 : size [-1,-2] / type 3
regular outputs:
- port 1 : size [-1,-2] / type 3
number/sizes of activation inputs: 0
number/sizes of activation outputs: 0
continuous-time state: no
discrete-time state: no
object discrete-time state: no
name of computational function: shift_32_LA
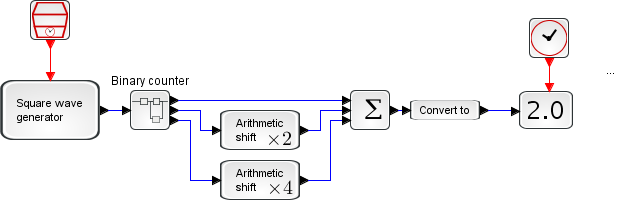
Example
In this example the Super block is a binary counter with 3 bits output. In order to obtain the corresponding decimal value,
the outputs Q1
and Q2 of the counter are respectively shifted left
of one bit and of two bits. Finally the Q0 output,
and the shifted outputs are added.
To better see the output change, set the parameter Real Time Scale to 0.5 in the Settings menu item of the Simulation menu. Open this example in Xcos
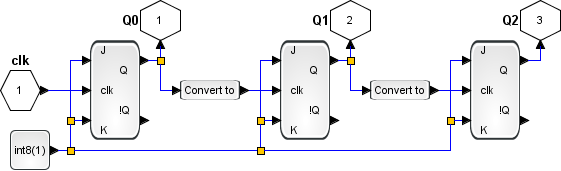
Below the details of the binary counter.
Interfacing function
Computational function
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_32_LA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_32_LC.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_32_RA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_u32_RA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_32_RC.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_16_LA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_16_LC.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_16_RA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_u16_RA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_16_RC.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_8_LA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_8_LC.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_8_RA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_u8_RA.c
SCI/modules/scicos_blocks/src/c/shift_8_RC.c
Authors
Fady NASSIF - INRIA
| << LOGIC | Integer palette | SRFLIPFLOP >> |