polyfit
Polynomial curve fitting
Syntax
p = polyfit(x, y, n) [p, S] = polyfit(x, y, n) [p, S, mu] = polyfit(x, y, n)
Arguments
- x
real or complex vector/matrix
- y
real or complex vector/matrix.
ymust have the same size asx- n
an integer, n>=0. It is a degree of the fitting polynomial. Or a polynom. In the case,
polyfitextracts the degree of polynom and returns a polynom containing the coefficients.- p
a
1xn+1real or complex vector or polynom, the polynomial coefficients- S
a structure containing the following fields:
- R
a matrix of doubles, the triangular factor R form the qr decomposition
- df
a real, the degrees of freedom
- normr
a real, the norm of the residuals
- mu
a
1x2vector.mu(1)ismean(x)andmu(2)isstdev(x)
Description
p = polyfit(x, y, n) returns a vector of coefficients of a polynomial p(x)
of degree n:
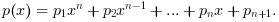
Depending on the type of n, p will be a real or complex vector or a polynom.
p can be used with polyval function to evaluate the polynomial at the data points.
[p, S] = polyfit(x, y, n) returns a vector of coefficients of a polynomial and a structure
S that can be used with polyval to compute the estimated error of the predicted values.
[p, S, mu] = polyfit(x, y, n) returns a third output argument mu
containing [mean(x), stdev(x)]. x is centered at zero and scaled to have unit standard deviation.
Examples
example 1 - p = polyfit(x, y, n)
x = 1:5; y = #(x) -> (-2*x.^4 + x.^3 - 5 * x.^2 + 6 *x -2); p = polyfit(x, y(x), 3) xx = linspace(1, 5, 100); yy = polyval(p, xx); plot(x, y(x), "b.", "thickness", 2); plot(xx, yy, "r");
example 2 - p = polyfit(x, y, n) with n a polynom
x = 1:5; y = #(x) -> (-2*x.^4 + x.^3 - 5 * x.^2 + 6 *x -2); p = polyfit(x, y(x), %s^3) xx = linspace(1, 5, 100); yy = polyval(p, xx); plot(x, y(x), "b.", "thickness", 2); plot(xx, yy, "r");
example 3 - [p, S, mu] = polyfit(x, y, n)
History
| Version | Description |
| 2025.0.0 | Introduction in Scilab. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << kmeans | Statistiques | polyval >> |