iir
iir digital filter
Syntax
hz=iir(n,ftype,fdesign,frq,delta) [p,z,g]=iir(n,ftype,fdesign,frq,delta)
Arguments
- n
positive number witn integer value, the filter order.
- ftype
string specifying the filter type, the possible values are:
'lp'for low-pass,'hp'for high pass,'bp'for band pass and'sb'for stop band.- fdesign
string specifying the analog filter design, the possible values are:
'butt','cheb1','cheb2'and'ellip'- frq
2-vector of discrete cut-off frequencies (i.e.,
0<frq<.5). For'lp'and'hp'filters onlyfrq(1)is used (in this case,frqcan be a scalar). For'bp'and'sb'filtersfrq(1)is the upper cut-off frequency andfrq(2)is the lower cut-off frequency.- delta
2-vector of error values for
cheb1,cheb2, andellipfilters where onlydelta(1)is used forcheb1case, onlydelta(2)is used forcheb2case, anddelta(1)anddelta(2)are both used forellipcase.0<delta(1),delta(2)<1for
cheb1filters1-delta(1)<ripple<1in passbandfor
cheb2filters0<ripple<delta(2)in stopbandfor
ellipfilters1-delta(1)<ripple<1in passband and0<ripple<delta(2)in stopband
- hz
a single input single output discrete transfer function, the low pass filter
- p
vector of transformed filter poles.
- z
vector of transformed filter zeros.
- g
a scalar: transformed filter gain.
Description
function which designs an iir digital filter using analog filter designs and bilinear transformation .
Examples
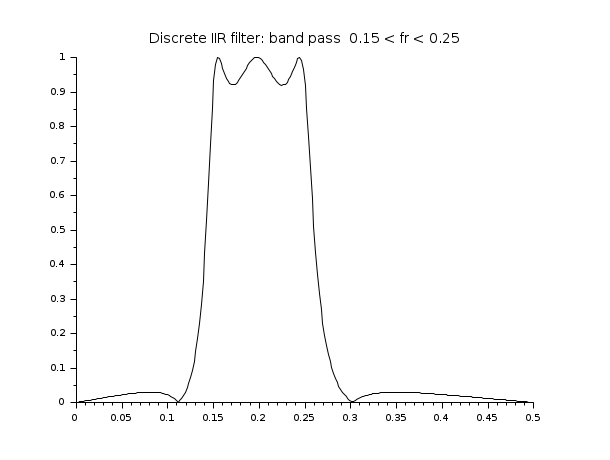
hz=iir(3,'bp','ellip',[.15 .25],[.08 .03]); [hzm,fr]=frmag(hz,256); plot2d(fr',hzm') xtitle('Discrete IIR filter: band pass 0.15 < fr < 0.25 ',' ',' '); q=poly(0,'q'); //to express the result in terms of the delay operator q=z^-1 hzd=horner(hz,1/q)
See also
| Report an issue | ||
| << hilbert | Filtrage | iirgroup >> |