h5read
Read the data of HDF5 dataset
Syntax
h5read(obj [, name, [, start, count [, stride [, block]]]]) h5read(filename, name [, start, count [, stride [, block]])
Arguments
- obj
a H5Object
- name
a string giving the path to the new dataset
- start
a row of doubles containing the start of the hyperslab
- count
a row of doubles containing the count of the hyperslab
- stride
a row of doubles containing the stride of the hyperslab
- block
a row of doubles containing the block of the hyperslab
- filename
a string giving the filename
Description
Read the content of a dataset according to the optional hyperslab selection.
It is possible to make an hyperslab selection on the data.
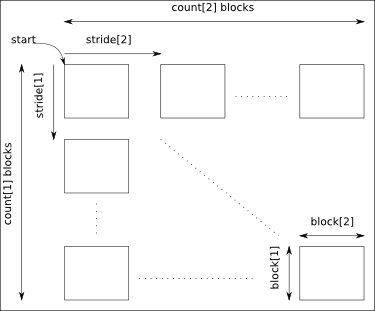
The arguments start, count, stride and block must have a size equal to the number of dimensions of the data:
- start: gives the coordinates in the data where to start the selection.
- count: gives the number of selected blocks in each dimension.
- stride: gives the shift between two consecutives blocks in each dimension. Take care that the stride must be greater than the corresponding block dimension.
- block: gives the block dimensions.
By default stride and block are set to 1 in each dimension.
Examples
x = int8(matrix(1:80, 10, 8)); save(TMPDIR + "/x.sod", "x"); // SOD files are HDF5 ones // Open the created file a = h5open(TMPDIR + "/x.sod"); // Read the data from the dataset 'x' dx = h5read(a, "/x") // Now select a part dx1 = h5read(a, "/x", [3 4], [5 3]) // ...which is equivalent to dx(3:(3+5-1),4:(4+3-1)) // We have finished so we free all the resources h5close(a);
See also
- h5readattr — Read the data of an HDF5 attribute
- h5write — Create a dataset (if it does not exist) and write the data
- h5dataset — Create a dataset and write the data
History
| Version | Description |
| 5.5.0 | HDF5 module introduced. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << h5open | Fichiers HDF5 | h5readattr >> |