fftshift
rearranges the fft output, moving the zero frequency to the center of the spectrum
Syntax
y = fftshift(x) y = fftshift(x, along)
Arguments
- x, y
vectors, matrices or hypermatrices, of same sizes.
- along
1 | "r" | 2 | "c" | 0<along<=ndims(x): dimension along which halves are switched.
Description
If x results of an fft computation, y=fftshift(x)
or y=fftshift(x,"all") moves the zero frequency component to the
center of the spectrum, which is sometimes a more convenient form.
x = [x1 x2 ] gives y = [x2 x1 ] // vector
[x11 x12] [x22 x21]
x = | | gives y = | | // matrix
[x21 x22] [x12 x11]
etc
y=fftshift(x,n) makes the swap only along the nth
dimension.
Examples
x = [1 2 3 4 5 6 7] fftshift(x)
--> x = [1 2 3 4 5 6 7] x = 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. --> fftshift(x) ans = 5. 6. 7. 1. 2. 3. 4.
x = matrix(1:36,6,6) fftshift(x) fftshift(x, "r") fftshift(x, "c")
--> x = matrix(1:36,6,6) x = 1. 7. 13. 19. 25. 31. 2. 8. 14. 20. 26. 32. 3. 9. 15. 21. 27. 33. 4. 10. 16. 22. 28. 34. 5. 11. 17. 23. 29. 35. 6. 12. 18. 24. 30. 36. --> fftshift(x) // Corners go to the center ans = 22. 28. 34. 4. 10. 16. 23. 29. 35. 5. 11. 17. 24. 30. 36. 6. 12. 18. 19. 25. 31. 1. 7. 13. 20. 26. 32. 2. 8. 14. 21. 27. 33. 3. 9. 15. --> fftshift(x, "r") // External rows become middle rows ans = 4. 10. 16. 22. 28. 34. 5. 11. 17. 23. 29. 35. 6. 12. 18. 24. 30. 36. 1. 7. 13. 19. 25. 31. 2. 8. 14. 20. 26. 32. 3. 9. 15. 21. 27. 33. --> fftshift(x, "c") // External columns become middle columns ans = 19. 25. 31. 1. 7. 13. 20. 26. 32. 2. 8. 14. 21. 27. 33. 3. 9. 15. 22. 28. 34. 4. 10. 16. 23. 29. 35. 5. 11. 17. 24. 30. 36. 6. 12. 18.
// Make a signal t = 0:0.1:1000; x = 3*sin(t)+8*sin(3*t)+0.5*sin(5*t)+3*rand(t); // Compute the fft y = fft(x,-1); // Display clf(); subplot(2,1,1); plot2d(abs(y)) subplot(2,1,2); plot2d(fftshift(abs(y)))
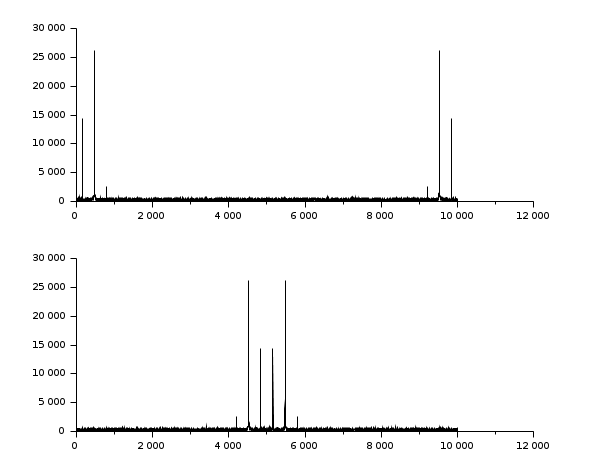
// Make a 2D image t = 0:0.1:30; x = 3*sin(t')*cos(2*t)+8*sin(3*t')*sin(5*t)+.. 0.5*sin(5*t')*sin(5*t)+3*rand(t')*rand(t); // Compute the fft y = fft(x,-1); // Display clf(); gcf().color_map = hotcolormap(256); subplot(2,1,1); Matplot(abs(y)) subplot(2,1,2); Matplot(fftshift(abs(y)))
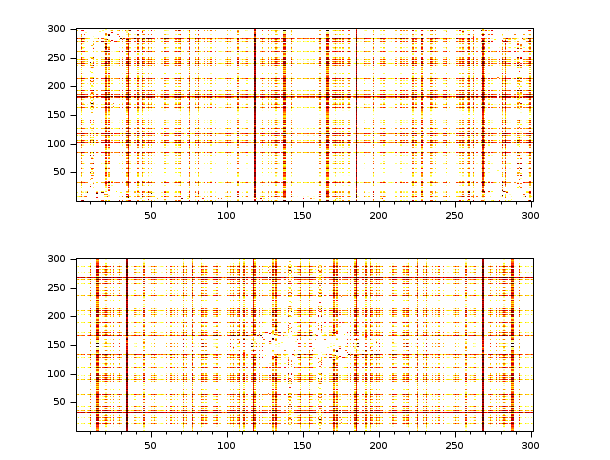
See also
- ifftshift — inverse de fftshift
- flipdim — inverse l'ordre des (blocs de) lignes, colonnes, pages.. d'un tableau.
- circshift — circularly shifts elements or subarrays of an array (regular, of structures, cells, custom)
- fft — Transformée de Fourier discrète directe ou inverse uni-, bi-, ou N-dimensionnelle
| Report an issue | ||
| << fft2 | Tranformées | hilb >> |