Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
xcorr
Computes discrete auto or cross correlation
Calling Sequence
[c [,lagindex]] = xcorr(x [,maxlags [,scaling]]) [c [,lagindex]] = xcorr(x,y [,maxlags [,scaling]])
Parameters
- x
a vector of real or complex floating point numbers.
- y
a vector of real or complex floating point numbers. The default value is
x.- maxlags
a scalar with integer value greater than 1. The default value is
n. Wherenis the maximum of thexandyvector length.- scaling
a character string with possible value:
"biased","unbiased","coeff","none". The default value is"none".- c
a vector of real or complex floating point numbers with same orientation as
x.- lagindex
a row vector, containing the lags index corresponding to the
cvalues.
Description
c=xcorr(x)computes the un-normalized discrete auto correlation: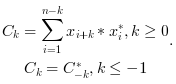 and return in
and return in
cthe sequence of auto correlation lags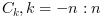 with
with
nis the length ofxxcorr(x,y)computes the un-normalized discrete cross correlation: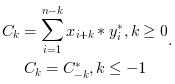 and return in
and return in
cthe sequence of auto correlation lags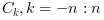 with
with
nis the maximum ofxandylength's.
If the maxlags argument is given
xcorr returns in c the sequence of
auto correlation lags 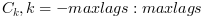 . If
. If
maxlags is greater than length(x),
the first and last values of c are zero.
The scaling argument decribes how
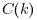 is normalized before being returned in
is normalized before being returned in
c:
- "biased":
c=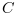
/n. - "unbiased":
c=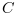
./(n-(-maxlags:maxlags)). - "coeff":
c=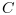
/(norm(x)*norm(y)).
Remark
The corr function computes the "biased" covariance ofx
and
y
and only return in
c
the sequence of auto correlation lags
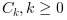 .
.Method
This function computes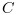 using
using
ifft(fft(x).*conj(fft(y))).Examples
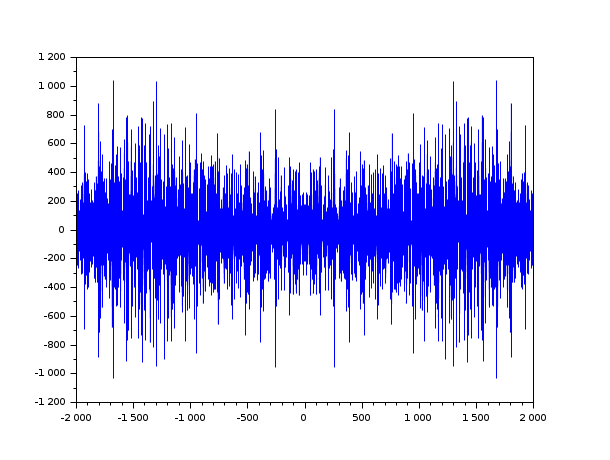
t = linspace(0, 100, 2000); y = 0.8 * sin(t) + 0.8 * sin(2 * t); [c, ind] = xcorr(y, "biased"); plot(ind, c)
Authors
- Serge Steer, INRIA
Used Functions
History
| Version | Description |
| 5.4.0 | xcorr added. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << wfir_gui | Signal Processing | xcov >> |