Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
besseli
Modified Bessel functions of the first kind (I sub alpha).
besselj
Bessel functions of the first kind (J sub alpha).
besselk
Modified Bessel functions of the second kind (K sub alpha).
bessely
Bessel functions of the second kind (Y sub alpha).
besselh
Bessel functions of the third kind (aka Hankel functions)
Calling Sequence
y = besseli(alpha,x [,ice]) y = besselj(alpha,x [,ice]) y = besselk(alpha,x [,ice]) y = bessely(alpha,x [,ice]) y = besselh(alpha,x) y = besselh(alpha,K,x [,ice])
Arguments
- x
real or complex vector.
- alpha
real vector
- ice
integer flag, with default value 0
- K
integer, with possible values 1 or 2, the Hankel function type.
Description
besseli(alpha,x)computes modified Bessel functions of the first kind (I sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.besseli(alpha,x,1)computesbesseli(alpha,x).*exp(-abs(real(x))).besselj(alpha,x)computes Bessel functions of the first kind (J sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.besselj(alpha,x,1)computesbesselj(alpha,x).*exp(-abs(imag(x))).besselk(alpha,x)computes modified Bessel functions of the second kind (K sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.besselk(alpha,x,1)computesbesselk(alpha,x).*exp(x).bessely(alpha,x)computes Bessel functions of the second kind (Y sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.bessely(alpha,x,1)computesbessely(alpha,x).*exp(-abs(imag(x))).besselh(alpha [,K] ,x)computes Bessel functions of the third kind (Hankel function H1 or H2 depending onK), for real orderalphaand argumentx. If omittedKis supposed to be equal to 1.besselh(alpha,1,x,1)computesbesselh(alpha,1,x).*exp(-%i*x)andbesselh(alpha,2,x,1)computesbesselh(alpha,2,x).*exp(%i*x)
Remarks
If alpha and x are arrays of
the same size, the result y is also that size. If
either input is a scalar, it is expanded to the other input's size. If one
input is a row vector and the other is a column vector, the
resulty is a two-dimensional table of function
values.
Y_alpha and J_alpha Bessel functions are 2 independent solutions of the Bessel 's differential equation :
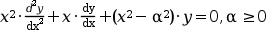
K_alpha and I_alpha modified Bessel functions are 2 independant solutions of the modified Bessel 's differential equation :
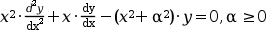
H^1_alpha and H^2_alpha, the Hankel functions of first and second kind, are linear linear combinations of Bessel functions of the first and second kinds:
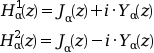
Examples
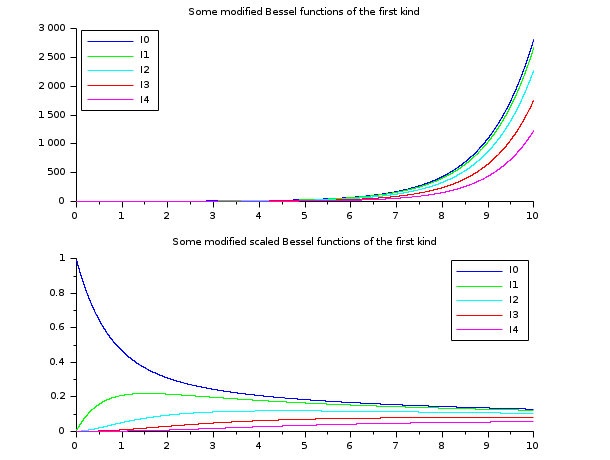
// besselI functions // ================== x = linspace(0.01,10,5000)'; clf() subplot(2,1,1) plot2d(x,besseli(0:4,x), style=2:6) legend('I'+string(0:4),2); xtitle("Some modified Bessel functions of the first kind") subplot(2,1,2) plot2d(x,besseli(0:4,x,1), style=2:6) legend('I'+string(0:4),1); xtitle("Some modified scaled Bessel functions of the first kind")
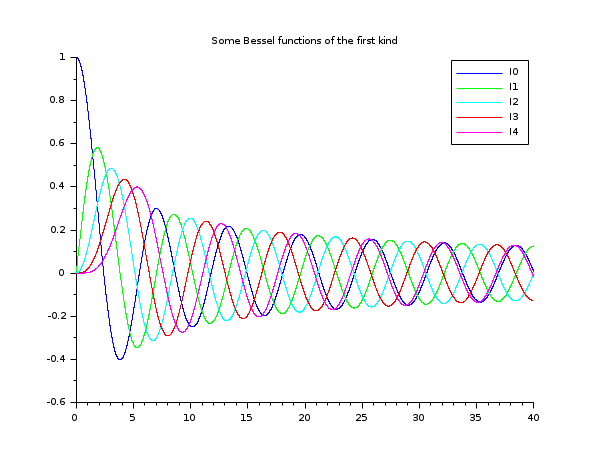
// besselJ functions // ================= clf() x = linspace(0,40,5000)'; plot2d(x,besselj(0:4,x), style=2:6, leg="J0@J1@J2@J3@J4") legend('I'+string(0:4),1); xtitle("Some Bessel functions of the first kind")
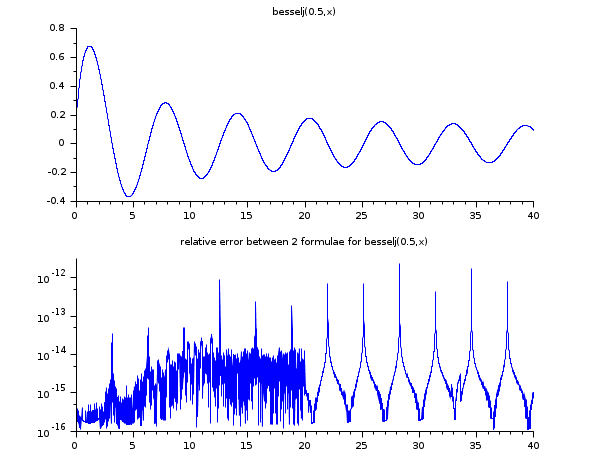
// use the fact that J_(1/2)(x) = sqrt(2/(x pi)) sin(x) // to compare the algorithm of besselj(0.5,x) with a more direct formula x = linspace(0.1,40,5000)'; y1 = besselj(0.5, x); y2 = sqrt(2 ./(%pi*x)).*sin(x); er = abs((y1-y2)./y2); ind = find(er > 0 & y2 ~= 0); clf() subplot(2,1,1) plot2d(x,y1,style=2) xtitle("besselj(0.5,x)") subplot(2,1,2) plot2d(x(ind), er(ind), style=2, logflag="nl") xtitle("relative error between 2 formulae for besselj(0.5,x)")
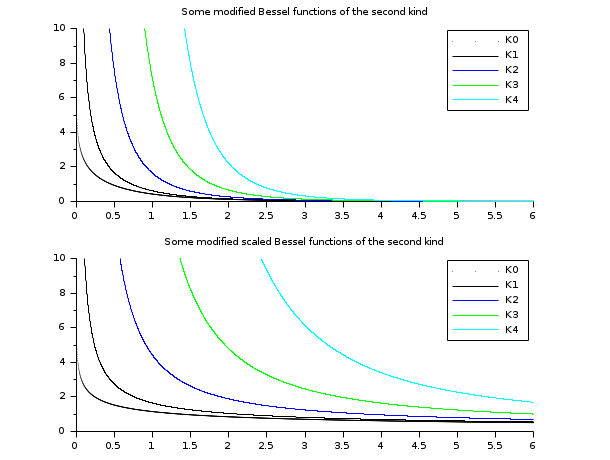
// besselK functions // ================= x = linspace(0.01,10,5000)'; clf() subplot(2,1,1) plot2d(x,besselk(0:4,x), style=0:4, rect=[0,0,6,10]) legend('K'+string(0:4),1); xtitle("Some modified Bessel functions of the second kind") subplot(2,1,2) plot2d(x,besselk(0:4,x,1), style=0:4, rect=[0,0,6,10]) legend('K'+string(0:4),1); xtitle("Some modified scaled Bessel functions of the second kind")
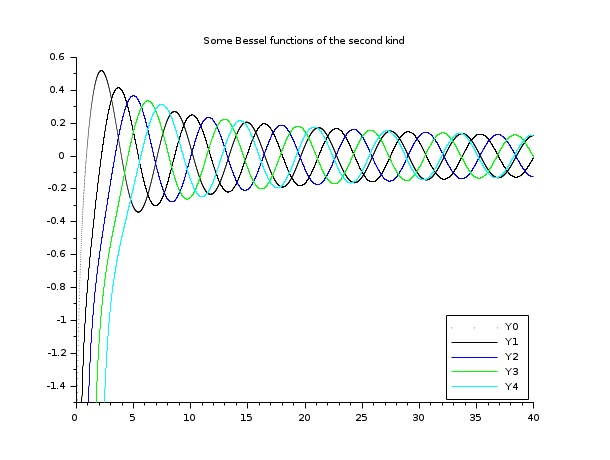
// besselY functions // ================= x = linspace(0.1,40,5000)'; // Y Bessel functions are unbounded for x -> 0+ clf() plot2d(x,bessely(0:4,x), style=0:4, rect=[0,-1.5,40,0.6]) legend('Y'+string(0:4),4); xtitle("Some Bessel functions of the second kind")
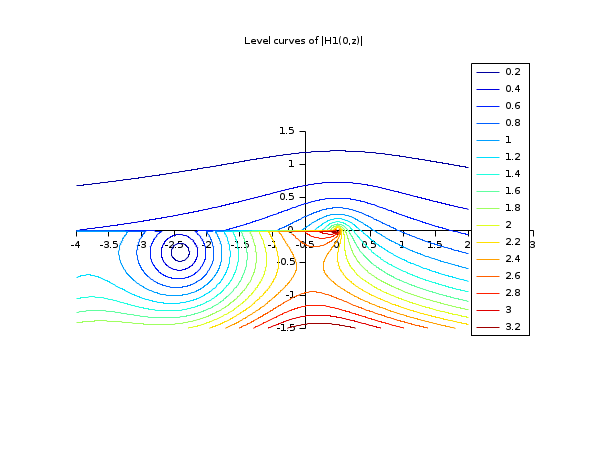
// besselH functions // ================= x=-4:0.025:2; y=-1.5:0.025:1.5; [X,Y] = ndgrid(x,y); H = besselh(0,1,X+%i*Y); clf();f=gcf(); xset("fpf"," ") f.color_map=jetcolormap(16); contour2d(x,y,abs(H),0.2:0.2:3.2,strf="034",rect=[-4,-1.5,3,1.5]) legends(string(0.2:0.2:3.2),1:16,"ur") xtitle("Level curves of |H1(0,z)|")
Used Functions
The source codes can be found in SCI/modules/special_functions/src/fortran/slatec and SCI/modules/special_functions/src/fortran
Slatec : dbesi.f, zbesi.f, dbesj.f, zbesj.f, dbesk.f, zbesk.f, dbesy.f, zbesy.f, zbesh.f
Drivers to extend definition area (Serge Steer INRIA): dbesig.f, zbesig.f, dbesjg.f, zbesjg.f, dbeskg.f, zbeskg.f, dbesyg.f, zbesyg.f, zbeshg.f
| Report an issue | ||
| << amell | Special Functions | beta >> |