xcov
Computes discrete auto or cross covariance
Syntax
[c, lagindex] = xcov(x) [c, lagindex] = xcov(x, y) [c, lagindex] = xcov(.., maxlags) [c, lagindex] = xcov(.., maxlags, scaling)
Parameters
- x
a vector of real or complex floating point numbers.
- y
a vector of real or complex floating point numbers. The default value is
x.- maxlags
a scalar with integer value greater than 1. The default value is
n. Wherenis the maximum of thexandyvector length.- scaling
a character string with possible value:
"biased","unbiased","coeff","none". The default value is"none".- c
a vector of real or complex floating point numbers with same orientation as
x.- lagindex
a row vector, containing the lags index corresponding to the
cvalues.
Description
c=xcov(x)computes the un-normalized discrete covariance:
and return in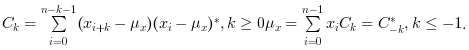
cthe sequence of covariance lags Ck=-n:n wherenis the length ofxxcov(x,y)computes the un-normalized discrete cross covariance:
and return in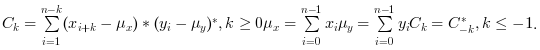
cthe sequence of cross covariance lags Ck=-n:n wherenis the maximum ofxandylength's.
If the maxlags argument is given
xcov returns in c the sequence of
covariance lags Ck=-maxlags:maxlags. If
maxlags is greater than length(x),
the first and last values of c are zero.
The scaling argument describes how
C(k) is normalized before being returned in
c:
- "biased":
c=C/n. - "unbiased":
c=C./(n-(-maxlags:maxlags)). - "coeff":
c=C/(norm(x)*norm(y)).
Remark
The corr function computes the "biased" covariance ofx and y and only return in c
the sequence of covariance lags Ck≥0
.Method
This function computes C usingxcorr(x-mean(x),y-mean(y),...).Examples
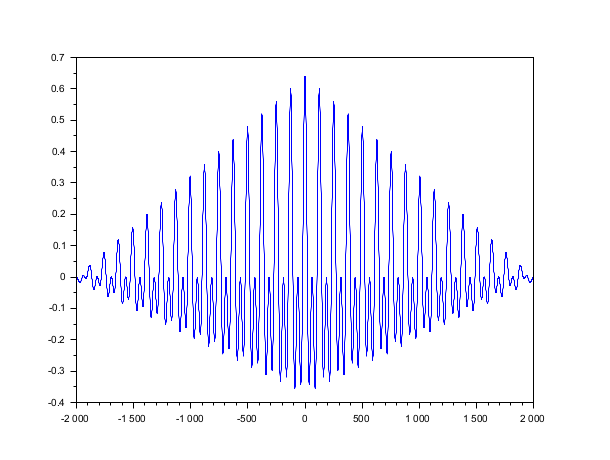
t = linspace(0, 100, 2000); y = 0.8 * sin(t) + 0.8 * sin(2 * t); [c, ind] = xcov(y, "biased"); plot(ind, c)
See also
History
| Version | Description |
| 5.4.0 | xcov added. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << unwrap | Signal Processing | FFTW >> |