Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
atand
2-quadrant and 4-quadrant element-wise inverse tangent, result in degree
Syntax
phi = atand(x) phi = atand(y, x)
Arguments
- x
a real scalar, vector or matrix.
- phi
a real scalar, vector or matrix.
- x, y
real scalars, vectors or matrices of the same size.
- phi
a real scalar, vector or matrix.
Description
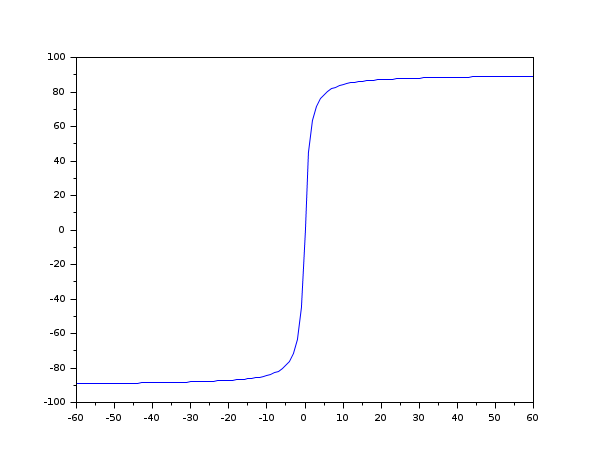
The first form computes the 2-quadrant inverse tangent, which is the
inverse of tand(phi). The
phi elements are in the interval
[-90, 90].
The second form computes the 4-quadrant arctangent (atan2 in
Fortran), this is, it returns the argument (angle) of the complex number
x+i*y. The range of atand(y,x) is
[-180, 180i].
Both forms yield identical values if
x>0.
Sample
See also
| Report an issue | ||
| << atan | Trigonometry | atanh >> |