Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
cumsum
soma cumulativa
Seqüência de Chamamento
y=cumsum(x) y=cumsum(x,'r') or y=cumsum(x,1) y=cumsum(x,'c') or y=cumsum(x,2)
Parâmetros
- x
vetor ou matrix (de reais ou complexos)
- y
vetor ou matrix (de reais ou complexos)
Descrição
Para um vetor ou uma matriz x,
y=cumsum(x) retorna em y a soma
cumulativa de todas as entradas de x tomadas coluna a
coluna.
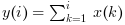
y=cumsum(x,'r') (ou, equivalentemente,
y=cumsum(x,1)) retorna em y a soma
cumulativa das linhas de x: y(:,i)=cumsum(x(:,i))
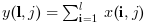
or
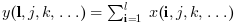
y=cumsum(x,'c') (ou, equivalentemente,
y=cumsum(x,2)) retorna em y a soma
cumulativa das colunas de x: y(i,:)=cumsum(x(i,:))
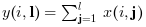
or
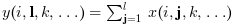
if orientation is equal to n then:
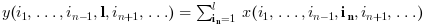
y=cumsum(x,"*") is equivalent to y=cumsum(x)
y=cumsum(x,'m') é a soma cumulativa ao longo da
primeira dimensão "não-singleton" de x (para
compatibilidade com o Matlab).
The outtype argument rules the way the summation is done:
For arrays of floats, of polynomials, of rational fractions, the evaluation is always done using floating points computations. The
"double"or"native"options are equivalent.For arrays of integers,
if
outtype="native"the evaluation is done using integer computations (modulo 2^b, where b is the number of bits used),if
outtype="double"the evaluation is done using floating point computations.The default value is
outtype="native".For arrays of booleans,
if
outtype="native"the evaluation is done using boolean computations ( + is replaced by |),if
outtype="double"the evaluation is done using floating point computations (%t values are replaced by 1 and %f values by 0).The default value is
outtype="double".
 | This function applies, with identical rules to sparse matrices. |
Exemplos
Ver Também
| Report an issue | ||
| << cumprod | Matrix operations | kron .*. >> |