Scilab 6.0.2
- Scilab Help
- Signal Processing
- Filters
- How to design an elliptic filter
- analpf
- buttmag
- casc
- cheb1mag
- cheb2mag
- ell1mag
- eqfir
- eqiir
- faurre
- ffilt
- filt_sinc
- filter
- find_freq
- frmag
- fsfirlin
- group
- hilbert
- iir
- iirgroup
- iirlp
- kalm
- lev
- levin
- lindquist
- remez
- remezb
- srfaur
- srkf
- sskf
- syredi
- system
- trans
- wfir
- wfir_gui
- wiener
- wigner
- window
- yulewalk
- zpbutt
- zpch1
- zpch2
- zpell
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
lev
Yule-Walker equations (Levinson's algorithm)
Syntax
[ar, sigma2, rc]=lev(r)
Arguments
- r
correlation coefficients
- ar
auto-Regressive model parameters
- sigma2
scale constant
- rc
reflection coefficients
Description
This function resolves the Yule-Walker equations using Levinson's algorithm. Generally, it is used to estimate the coefficients of an autoregressive process.
Example
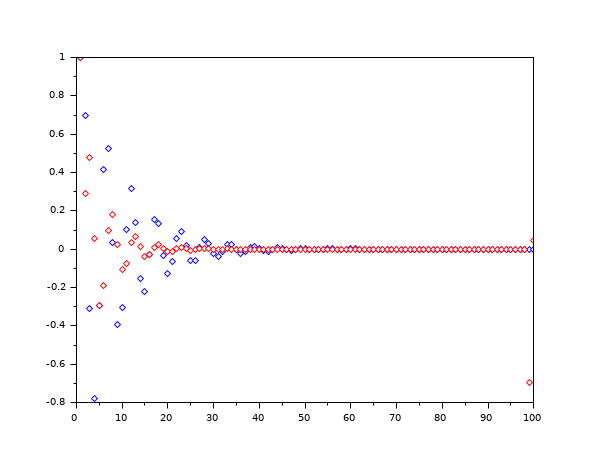
b=1; //numerator a=[1 -0.7 0.8]; //denominator x=[1 zeros(1,99)]; //input=impulse data=filter(b,a,x); //real data a2=lev(data); //modelized data a2=a2/a2(1); //normalization m_data=filter(1,a2,x); // Compare real data and modelized data plot(data,"color","blue","lineStyle","none","marker","d"); plot(m_data,"color","red","lineStyle","none","marker","d");
| Report an issue | ||
| << kalm | Filters | levin >> |