Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
h5read
Read the data of HDF5 dataset
Syntax
h5read(obj [, name, [, start, count [, stride [, block]]]]) h5read(filename, name [, start, count [, stride [, block]])
Arguments
- obj
a H5Object
- name
a string giving the path to the new dataset
- start
a row of doubles containing the start of the hyperslab
- count
a row of doubles containing the count of the hyperslab
- stride
a row of doubles containing the stride of the hyperslab
- block
a row of doubles containing the block of the hyperslab
- filename
a string giving the filename
Description
Read the content of a dataset according to the optional hyperslab selection.
It is possible to make an hyperslab selection on the data.
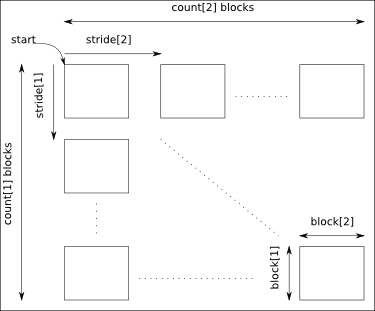
The arguments start, count, stride and block must have a size equal to the number of dimensions of the data:
- start: gives the coordinates in the data where to start the selection.
- count: gives the number of selected blocks in each dimension.
- stride: gives the shift between two consecutives blocks in each dimension. Take care that the stride must be greater than the corresponding block dimension.
- block: gives the block dimensions.
By default stride and block are set to 1 in each dimension.
Examples
x = int8(matrix(1:80, 10, 8)); save(TMPDIR + "/x.sod", "x"); // SOD files are HDF5 ones // Open the created file a = h5open(TMPDIR + "/x.sod"); // Read the data from the dataset 'x' dx = h5read(a, "/x") // Now select a part dx1 = h5read(a, "/x", [3 4], [5 3]) // ...which is equivalent to dx(3:(3+5-1),4:(4+3-1)) // We have finished so we free all the resources h5close(a);
See also
- h5readattr — Read the data of an HDF5 attribute
- h5write — Create a dataset (if it does not exist) and write the data
- h5dataset — Create a dataset and write the data
History
| Version | Description |
| 5.5.0 | HDF5 module introduced. |
| Report an issue | ||
| << h5open | HDF5 Management | h5readattr >> |