Scilab 6.0.1
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
hank
covariance to hankel matrix
Syntax
hk =hank(m, n, cov)
Arguments
- m
number of bloc-rows
- n
number of bloc-columns
- cov
sequence of covariances; it must be given as :[R0 R1 R2...Rk]
- hk
computed hankel matrix
Description
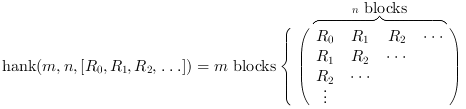
This function builds the hankel matrix of size
(m*d,n*d) from the covariance sequence of a vector
process. More precisely:
This function builds the hankel matrix of size (m*d,n*d)
from the covariance sequence of a vector process. More precisely:
Examples
//Example of how to use the hank macro for //building a Hankel matrix from multidimensional //data (covariance or Markov parameters e.g.) // //This is used e.g. in the solution of normal equations //by classical identification methods (Instrumental Variables e.g.) // //1)let's generate the multidimensional data under the form : // C=[c_0 c_1 c_2 .... c_n] //where each bloc c_k is a d-dimensional matrix (e.g. the k-th correlation //of a d-dimensional stochastic process X(t) [c_k = E(X(t) X'(t+k)], ' //being the transposition in scilab) // //we take here d=2 and n=64 c = rand(2, 2 * 64) //generate the hankel matrix H (with 4 bloc-rows and 5 bloc-columns) //from the data in c H = hank(4, 5, c);
See also
- toeplitz — matrice de Toeplitz, à bandes diagonales constantes choisies
| Report an issue | ||
| << corr | Corrélation de Convolution | xcorr >> |