Scilab 6.0.0
Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
geom3d
3次元プロットの後に3次元から2次元へ投影する
呼び出し手順
[x,y]=geom3d(x1,y1,z1)
引数
- x1,y1,z1
同じ大きさの実数ベクトル (3次元の点).
- x,y
x1,y1およびz1と同じ 大きさの実数ベクトル.
説明
geom3dは,
plot3d, plot3d1 または param3d
のような3次元プロット関数の後に使用され,
3次元空間(x1(i),y1(i),z1(i))
における点と投影された二次元平面上の対応する点(x(i),y(i))
の間のマッピングを行ないます.
この後,(x,y)に行う全ての2次元グラフィックプリミティブを
この3次元プロット上への重ね合わせるために使用できます.
例
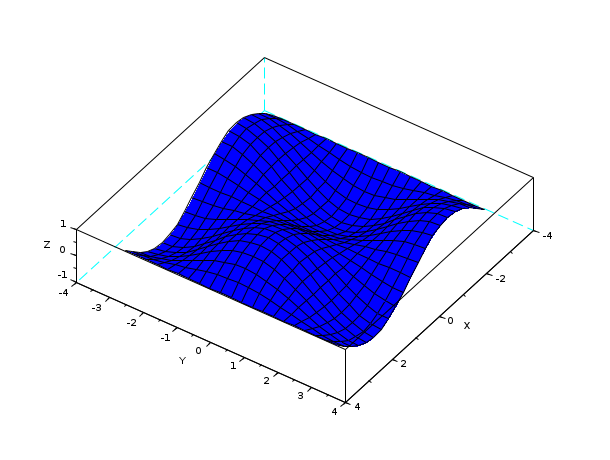
deff("[z]=surface(x,y)","z=sin(x)*cos(y)") t=%pi*(-10:10)/10; // 曲面の3次元プロット fplot3d(t,t,surface,35,45,"X@Y@Z") // ここで, (t,t,sin(t).*cos(t))は曲面上の曲線で, // geom3d および xpolyにより描画される [x,y]=geom3d(%pi/2,0,surface(%pi/2,0))
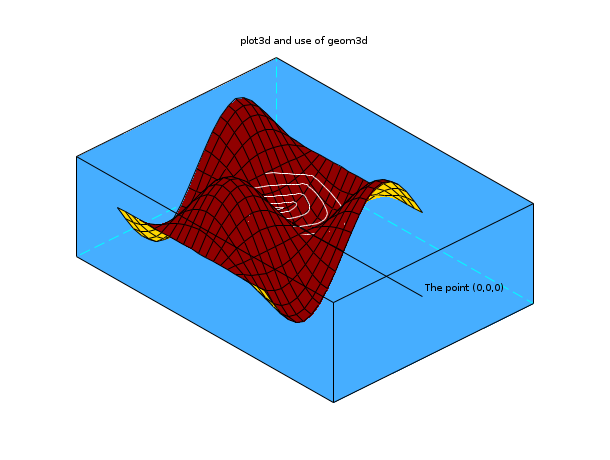
my_plot_desc = "plot3d and use of geom3d"; r = (%pi):-0.01:0; x = r.*cos(10*r); y = r.*sin(10*r); deff("[z]=Surf(x,y)","z=sin(x)*cos(y)"); t=%pi*(-10:10)/10; // 曲面をプロット fplot3d(t,t,Surf,35,45,"X@Y@Z",[19,2,3]); // 3次元グラフィック上に2次元グラフィックを追加 z=(sin(x).*cos(y)); [x1,y1] = geom3d(x,y,z); xpoly(x1,y1,"lines"); // いくつかのプロット用パラメータを調整 BackgroundColorId = color(70,174,255); current_axe = gca(); plot_3d = current_axe.children(2); plot_3d.hiddencolor = 32; polyline = current_axe.children(1)';; polyline.foreground = 8; current_axe.rotation_angles = [70,47]; current_axe.background = BackgroundColorId; // 2番目の2次元グラフィック [x1,y1] = geom3d([0,0],[0,0],[5,0]); xsegs(x1,y1); xstring(x1(1),y1(1),"The point (0,0,0)"); xtitle(my_plot_desc," "," "," ");
| Report an issue | ||
| << genfac3d | 3d_plot | hist3d >> |