Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
SRFLIPFLOP
SR flip-flop
Block Screenshot
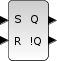
Contents
Palette
Description
This block describes the simplest and the most fundamental latch the SR flip flop. The output Q depends of the state of the inputs S and R. The output !Q is the logical negation of Q
If S (Set) is pulsed high while R is held low, then the Q output is forced high, and stays high when S returns low.
if R (Reset) is pulsed high while S is held low, then the Q output is forced low, and stays low when R returns low.
When S and R are low, Q(t) takes the value of the previous output state Q(t-1).
When S and R are both high, both Q and !Q take the low or high values; the state is unstable. Practically this case is forbidden.
The user can set the initial output state with Initial Value parameter.
This block is almost used as a memory
The truth table of this block is:
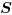 |
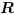 |
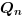 |
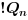 |
|
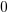 |
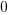 |
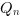 |
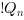 |
Hold |
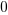 |
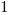 |
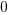 |
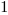 |
Reset |
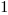 |
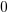 |
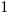 |
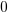 |
Set |
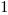 |
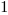 |
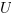 |
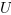 |
Forbidden state |
where
U
stands for "Unknown".
Data types
The block supports the following types :
Inputs:
R: scalar. Scilab's int8 data type only.
S: scalar. Scilab's int8 data type only.
A positive input is considered as logical 1, a negative or a null input as logical 0.
Outputs: scalar. Scilab's int8 data type.
Dialog box
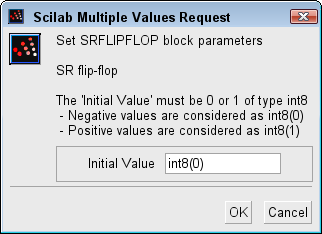
Initial Value
Initial Value of the state Q. It must be int8 data type.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1.
Default properties
always active: no
direct-feedthrough: yes
zero-crossing: no
mode: no
regular inputs:
- port 1 : size [1,1] / type 5
- port 2 : size [1,1] / type 5
regular outputs:
- port 1 : size [1,1] / type 5
- port 2 : size [1,1] / type 5
number/sizes of activation inputs: 0
number/sizes of activation outputs: 0
continuous-time state: no
discrete-time state: no
object discrete-time state: no
name of computational function: csuper
Example
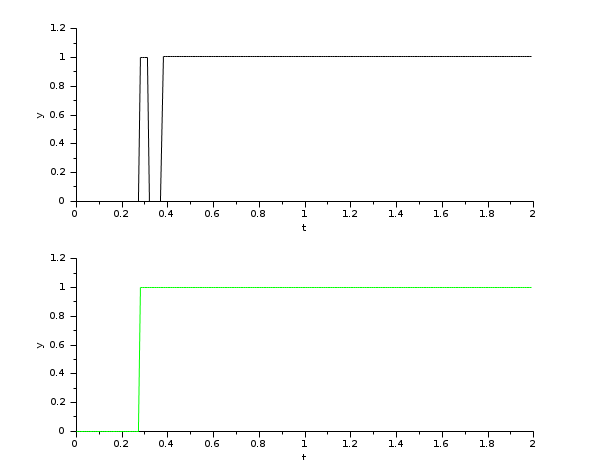
The following example presents a typical anti-bouncing application of the SR flipflop. The output graph shows the memory effect of the flipflop. Open this example in Xcos
Interfacing function
See also
- DLATCH — D latch flip-flop
- DFLIPFLOP — D flip-flop
- JKFLIPFLOP — JK flip-flop
| Report an issue | ||
| << SHIFT | Integer palette | Lookup tables palette >> |
