Please note that the recommended version of Scilab is 2026.0.1. This page might be outdated.
See the recommended documentation of this function
JKFLIPFLOP
JK flip-flop
Block Screenshot
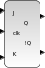
Contents
Palette
Description
The JK flip flop is the most versatile of the basic flip-flops. It has two inputs traditionally labeled J (Set) and K (Reset).
When the inputs J and K are different, the output Q takes the value of J at the next falling edge.
When the inputs J and K are both low, no change occurs in the output state.
When the inputs are both high the output Q will toggle from one state to other. It can perform the functions of the set/reset (SR) flip-flop and has the advantage that there are no ambiguous states.
The !Q output is the logical negation of Q
It can also act as a T flip-flop to accomplish toggling action if J and K are tied together. This toggle application finds extensive use in binary counters.
The user can set the initial output state with Initial Value parameter.
The truth table of this block is:
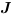 |
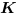 |
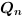 |
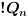 |
|
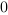 |
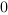 |
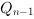 |
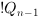 |
Hold |
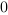 |
 |
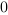 |
 |
Reset |
 |
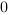 |
 |
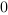 |
Set |
 |
 |
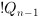 |
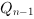 |
Toggle |
where Qn-1 is the previous state of
Qn.
Data types
The block supports the following types :
Inputs:
J: scalar. Scilab's int8 data type only.
clk: scalar. Scilab's real double.
K: scalar. Scilab's int8 data type only.
A positive input is considered as logical 1, a negative or a null input as logical 0.
Outputs: scalar. Scilab's int8 data type.
Dialog box
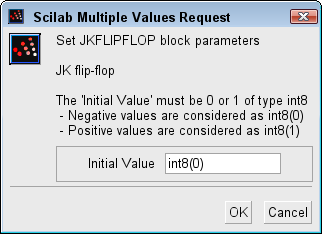
Initial Value
Initial state of the Q output.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1.
Default properties
always active: no
direct-feedthrough: yes
zero-crossing: no
mode: no
regular inputs:
- port 1 : size [1,1] / type 5
- port 2 : size [1,1] / type 1
- port 3 : size [1,1] / type 5
regular outputs:
- port 1 : size [1,1] / type 5
- port 2 : size [1,1] / type 5
number/sizes of activation inputs: 0
number/sizes of activation outputs: 0
continuous-time state: no
discrete-time state: no
object discrete-time state: no
name of computational function: csuper
Example
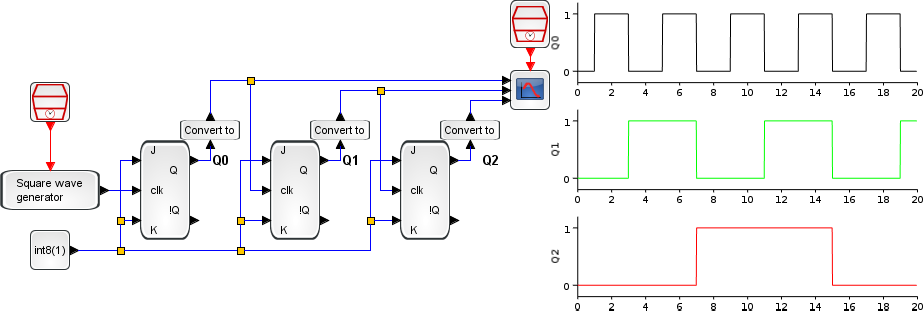
The following example builds a 3 bits asynchronous counter with JK flipflops wired as T flipflops. You can show on the
right the timing diagram of the Q0
to Q2 outputs of counter.
Open this example in Xcos
Interfacing function
See also
- DLATCH — D latch flip-flop
- DFLIPFLOP — D flip-flop
- SRFLIPFLOP — SR flip-flop
Authors
Fady NASSIF - INRIA
| << INTMUL | Integer palette | LOGIC >> |