barhomogenize
homogenize all the bars included in the current working axes
Syntax
barhomogenize() barhomogenize(h) barhomogenize([h,] style) barhomogenize([h,] width) barhomogenize([h,] style, width)
Arguments
- h
an axes handle: The axes where barhomogenize() must be applied. Default
h=gca().- style
word
'grouped'(default) or'stacked'- width
a decimal number
0 < width <= 1, setting the width of bars, as a fraction of the maximum allowed width. Default: 0.8.
Description
If there are several bar calls, the barhomogenize function
allows to homogenize the width and style of all bars (i.e which has the
polyline_style type 6) included in the current working axes.
These bars must have the same x data.
barhomogenize( ) : takes the default values h=gca(),
width=0.8, style='grouped'.
barhomogenize(h,...) : defines the current axes where the
drawing is performed.
barhomogenize(...,style,...) : defines how the bars are
drawn. The 'grouped' option allows to center the M polylines versus each
components of x, and the 'stacked' option allows to stack them.
barhomogenize(...,width) : defines the width of the
bar(s) in percentage (generally: 0<width<=1).
Examples
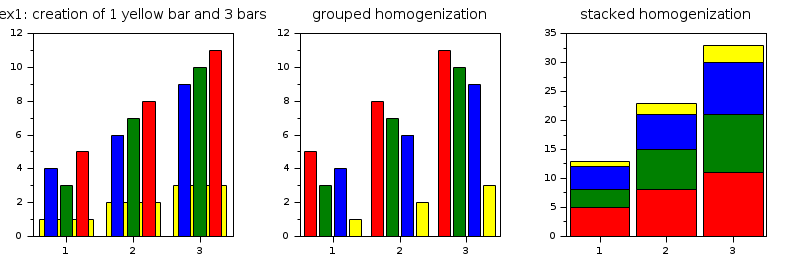
First example: creation of 1 yellow bar (i.e 1 polyline with polyline_style=6) and 3 bars (i.e 3 polylines with polyline_style=6)
subplot(2,3,1) xtitle('ex1: creation of 1 yellow bar and 3 bars') x=1:3; y1=1:3; y2=[4 3 5;6 7 8;9 10 11]; bar(x,y1,'yellow');bar(x,y2); // grouped homogenization of these 4 bars subplot(2,3,2) xtitle('grouped homogenization') x=1:3; y1=1:3; y2=[4 3 5;6 7 8;9 10 11]; bar(x,y1,'yellow');bar(x,y2); barhomogenize(); // stacked homogenization of the 4 bars subplot(2,3,3) xtitle('stacked homogenization') x=1:3; y1=1:3; y2=[4 3 5;6 7 8;9 10 11]; bar(x,y1,'yellow');bar(x,y2); barhomogenize('stacked',1);
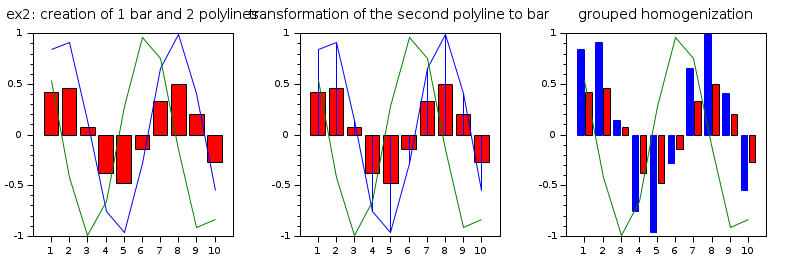
Second example :creation of 1 red bar (i.e 1 polyline with polyline_style=6) and 2 polylines with type=1 (calling plot function).
subplot(2,3,4) xtitle('ex2: creation of 1 bar and 2 polylines') x=1:10; y=sin(x)/2; bar(x,y,'red') x1=1:10; y1=[sin(x);cos(x)] plot(x1',y1') // modify the polyline_style type of the second polyline from plot (this polyline becomes a bar) subplot(2,3,5) xtitle('transformation of the second polyline to bar') x=1:10; y=sin(x)/2; bar(x,y,'red') x1=1:10; y1=[sin(x);cos(x)] plot(x1',y1') e=gce(); e2=e.children(2); e2.polyline_style=6; // homogenization of the first bar (from bar function) and second bar (from the modification). subplot(2,3,6) xtitle('grouped homogenization') x=1:10; y=sin(x)/2; bar(x,y,'red') x1=1:10; y1=[sin(x);cos(x)] plot(x1',y1') e=gce(); e2=e.children(2); e2.polyline_style=6; barhomogenize(); // change the style and the width //barhomogenize('stacked',0.5); //barhomogenize('stacked',1);
See also
- bar — bar histogram
- histplot — plot a histogram
- polyline_properties — description of the Polyline entity properties
| Report an issue | ||
| << barh | bar_histogram | Datatips >> |